How do I recover data from a FAT file system
The FAT file system derives his name from its main component: the File Allocation Table. This file system has been around since the 1980s. Microsoft promoted it through its DOS and Windows operating systems.
How Does The FAT File System Work?
Originally, using 8 bits per entry, it has evolved into versions FAT12, FAT16 and FAT32, each using 12, 16 and 32 bits respectively. Usually, Microsoft doesn’t differentiate between the older versions, and refers to them as FAT.
The main element of this file system is the File Allocation Table (FAT), which is allocated at formatting time. The FAT system divides the storage space into clusters. The FAT table contains entries for each cluster. For used clusters, each entry contains the number of the next cluster, or an end-of-file marker. Otherwise, it differentiates between unused and reserved clusters. Reserved are special clusters used by the operating system.
Directories are described in the same table. In the case of the root directory, the FAT table contains the number of the first cluster of each file in that directory. Using it, the operating system can build a cluster chain until it reaches the end-of-file marker. Sub-directories are treated in a similar manner.
The FAT32 file system has maximum file size of 4G limitation, which is due to the length of the entry in the directory table.
Overall, the FAT file system architecture is simple, efficient and has passed the test of time. It is still in use, being the default file system in many re
movable storage devices, such as USB sticks, flash and solid state memory cards, and many more.
Basically all operating systems consider it. Apple computers, using the MacOS X operating system, support it on volumes other that the boot disk. FAT is thus, the most widespread file system architecture.
Main Differences Between FAT12, FAT16, and FAT32
The main difference between the different FAT file system versions is the size of the volumes you can create. As FAT developed, the supported volume sizes increased. Here are the volume sizes for each version:
- FAT12 supports volume sizes up to 32 MB.
- FAT16 supports volume sizes up to 4 GB.
- FAT32 supports volume sizes up to 16 TB.
The FAT32 file system is commonly used on flash drives due to its support for multiple operating systems. However, one drawback it has against other file systems is that it can only store files up to 4GB. This is why you’ll find that some cameras split long recordings into 4GB chunks to ensure they’re written.
How to Recover Data from FAT16/FAT32/exFAT Hard Drive:
Deleting a file in the FAT file system simply means removing it from the FAT table. The data remains untouched until the clusters are overwritten by another file. As a result, deleted data can be recovered with some FAT recovery software before the storage space is used again.
Recover Using Disk Drill Data Recovery
Disk Drill is available for Windows and Mac computers. The Basic version is available for free download. The full version is commercial. Both versions can be used to retrieve lost files from a storage device using the FAT file system.
You can use one of two scan types with Disk Drill: Quick or Deep. The Quick scan does a basic scan of your FAT drive, while a Deep scan takes a thorough look at the whole drive. The results are presented together with a menu with options to select different file types. In addition, it can filter according to size and date. The scanning can be paused at any time and continued later. The session can also be saved for later use.
Follow these steps to recover data from a FAT drive using Disk Drill:
- Download and install Disk Drill.
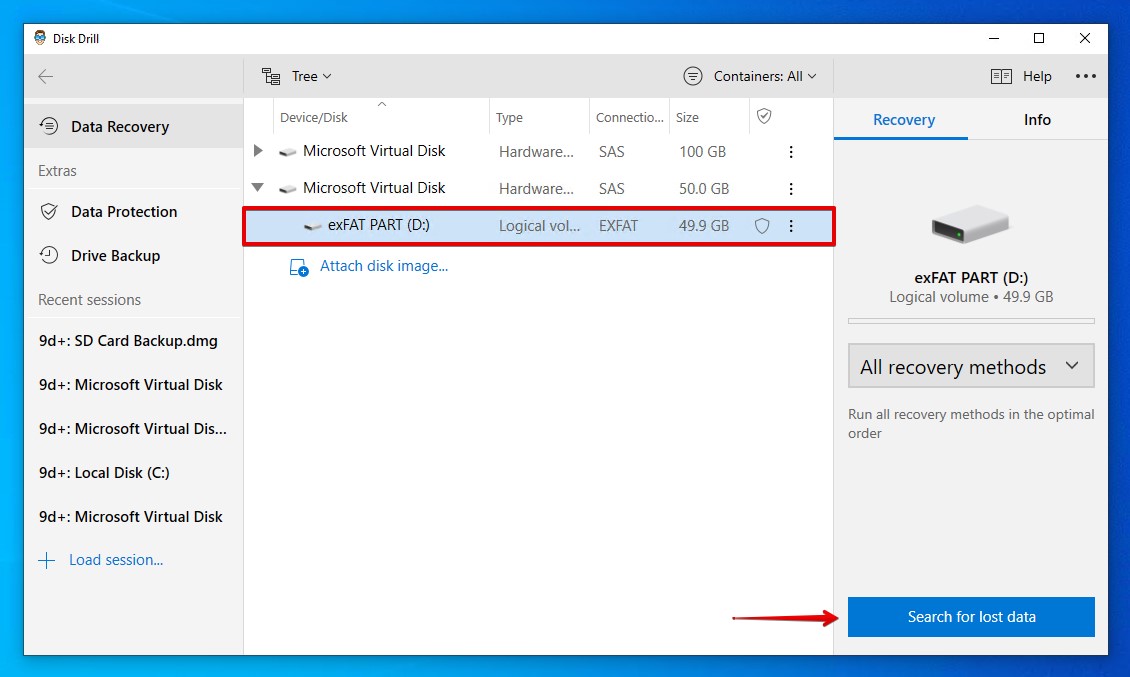
- Select the FAT drive or partition. If recovering from a disk image, attach the disk image using the Attach disk image option first. Once selected, click Search for lost data.
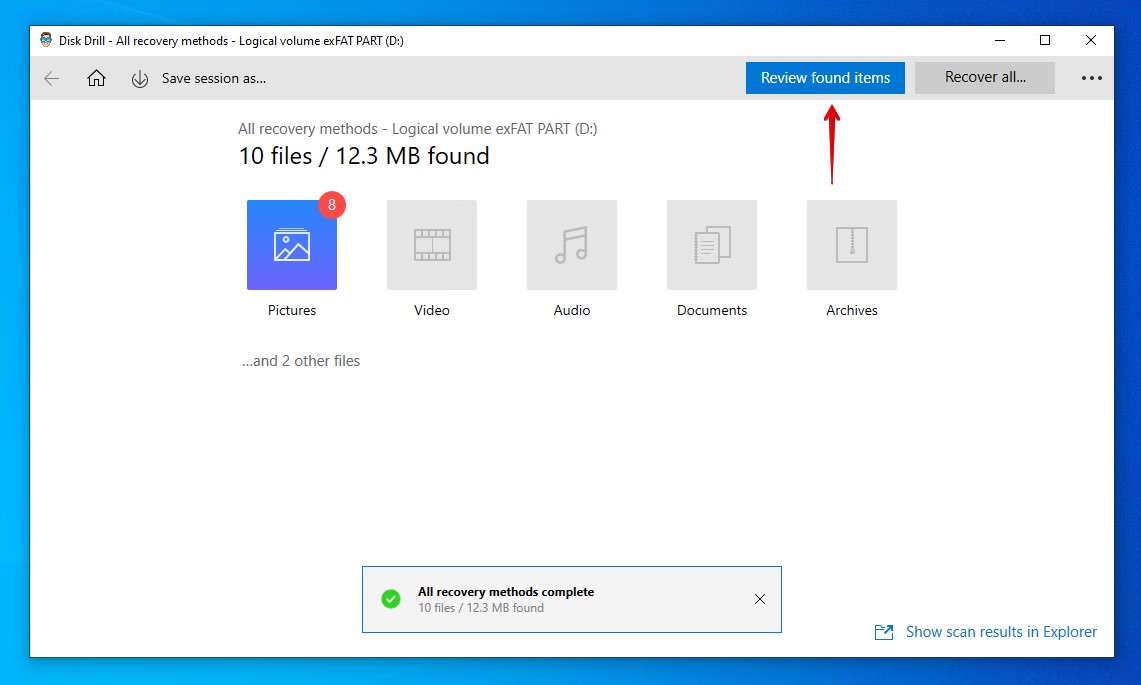
- Click Review found items to check what Disk Drill found in its scan.
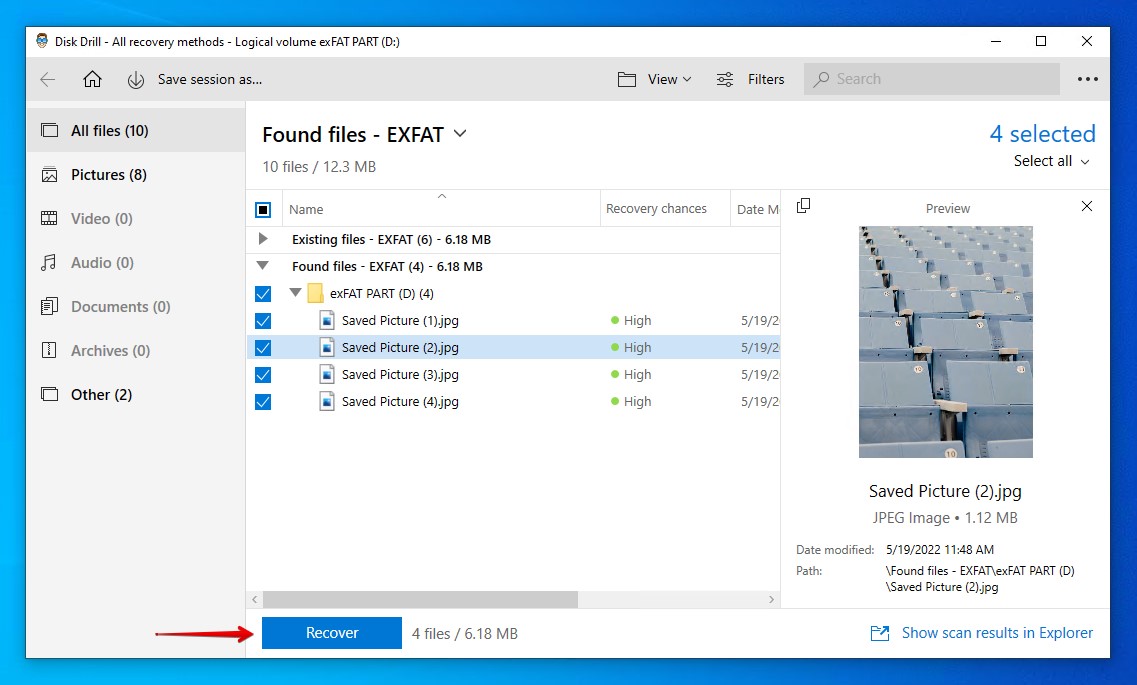
- Mark the files you want to recover. You can narrow your search using the search bar or by choosing the file type you want to view on the left. When you’re ready, click Recover.
- Choose where you want to store the recovered files. Make sure you’re not recovering to the same drive you’re recovering from. Click OK.
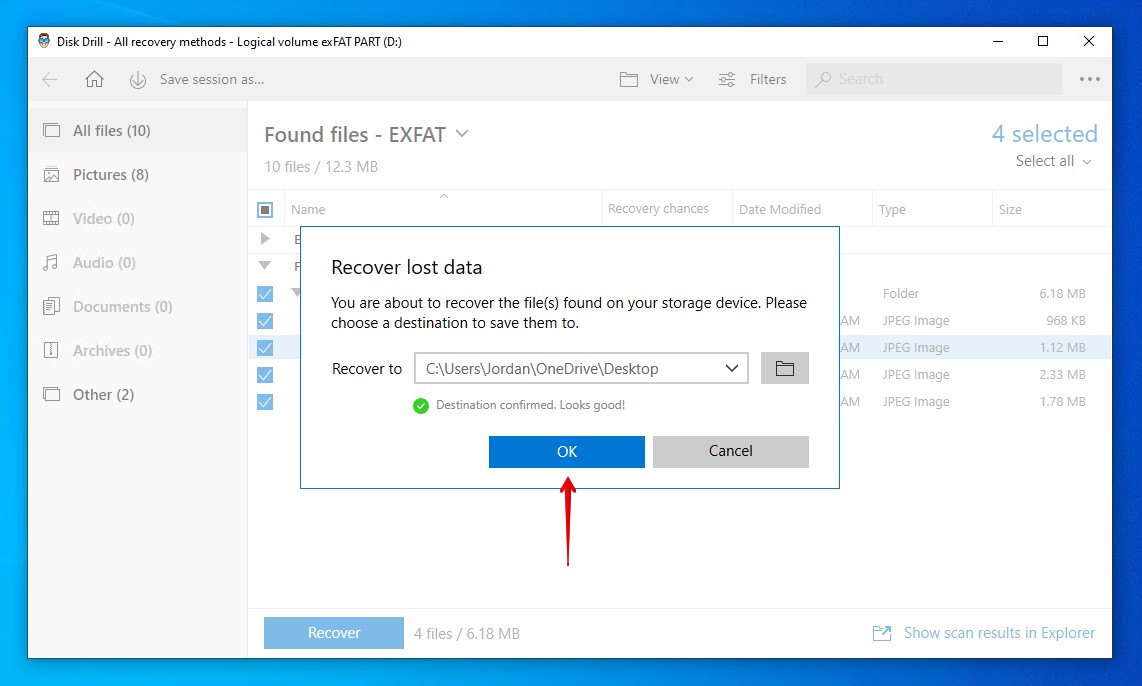
Recover Using TestDisk
TestDisk is a completely free data recovery tool. Unlike its partner tool PhotoRec which specializes in the recovery of individual data, TestDisk is able to recover entire partitions. It’s a popular go-to as it’s trusted and robust. It supports the recovery of multiple file systems, including FAT, exFAT, NTFS, and ext2.
As it’s a command-line tool, it can be difficult for some users. However, by following the steps below, you can recover data from your FAT drive using TestDisk:
- Download and unzip the TestDisk files. Open testdisk_win.
- Press Enter on the Create option.
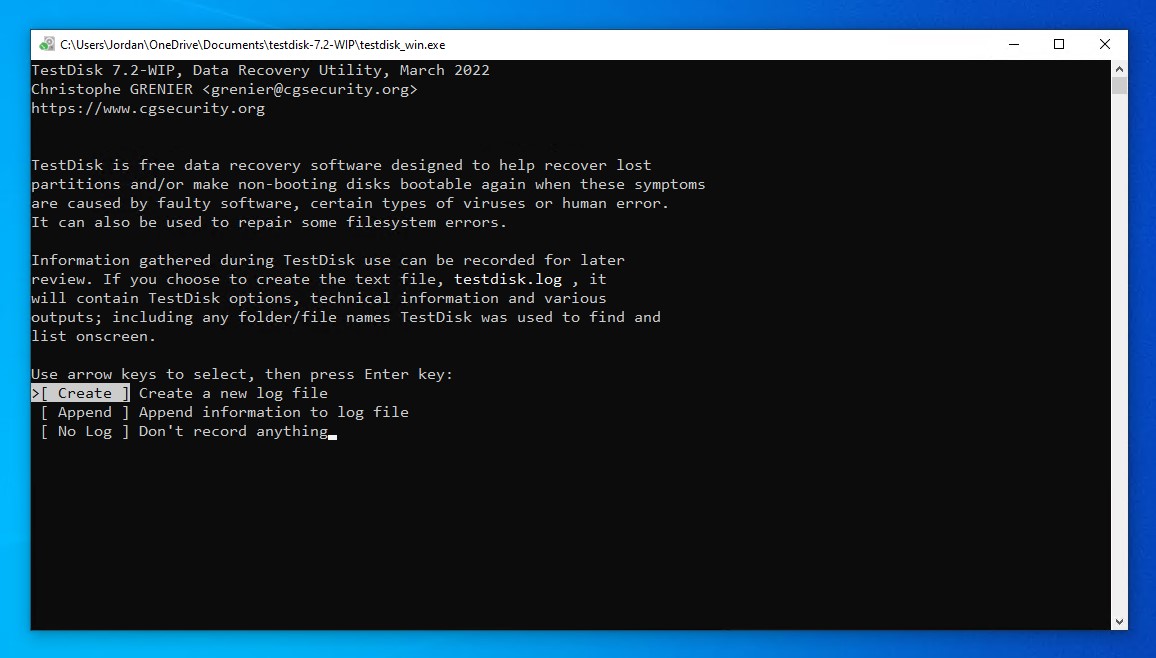
- Select the drive that contains the FAT partition, then press Enter.
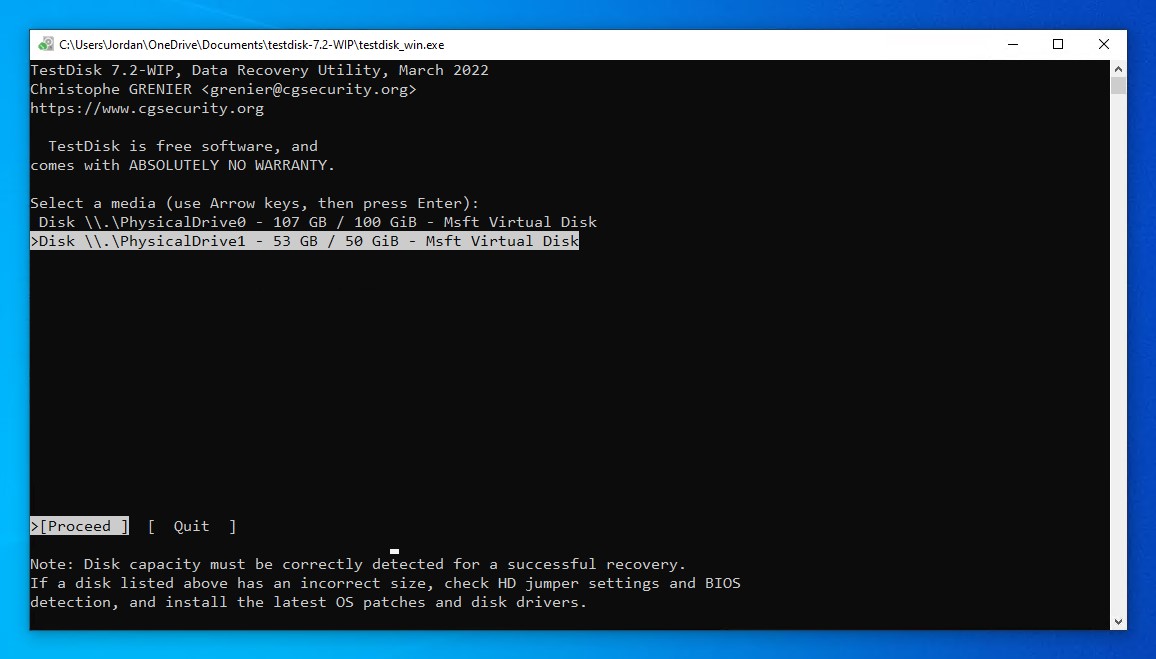
- Select your partition table type. TestDisk generally auto-detects this if you’re unsure. Press Enter.
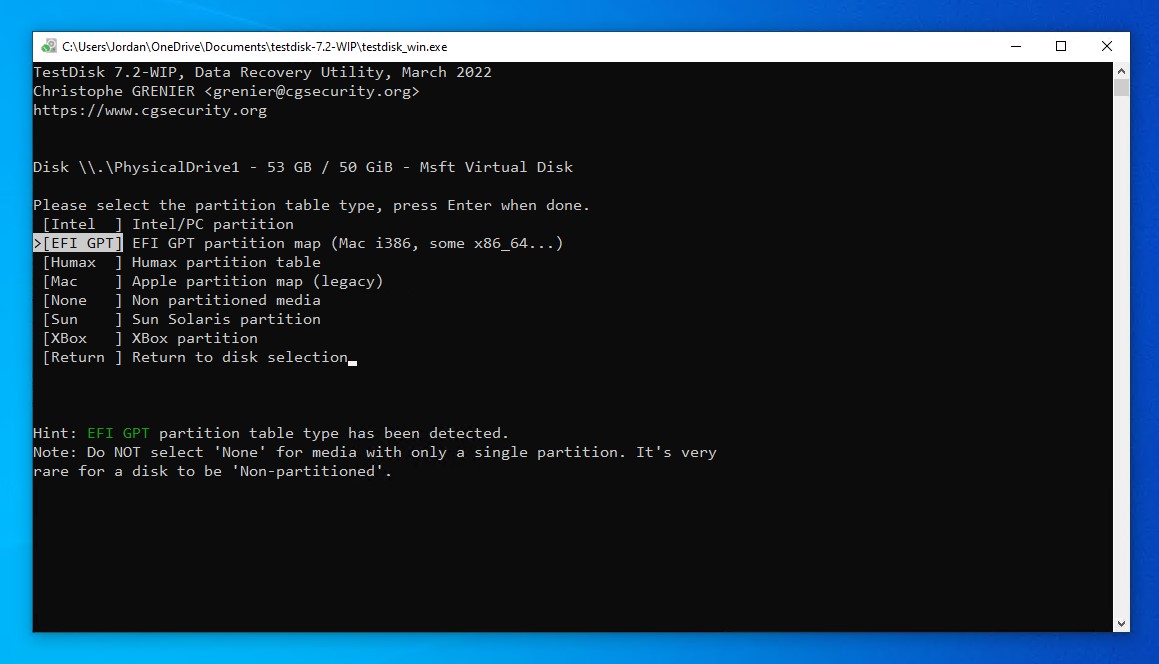
- Press Enter on the Analyse option.
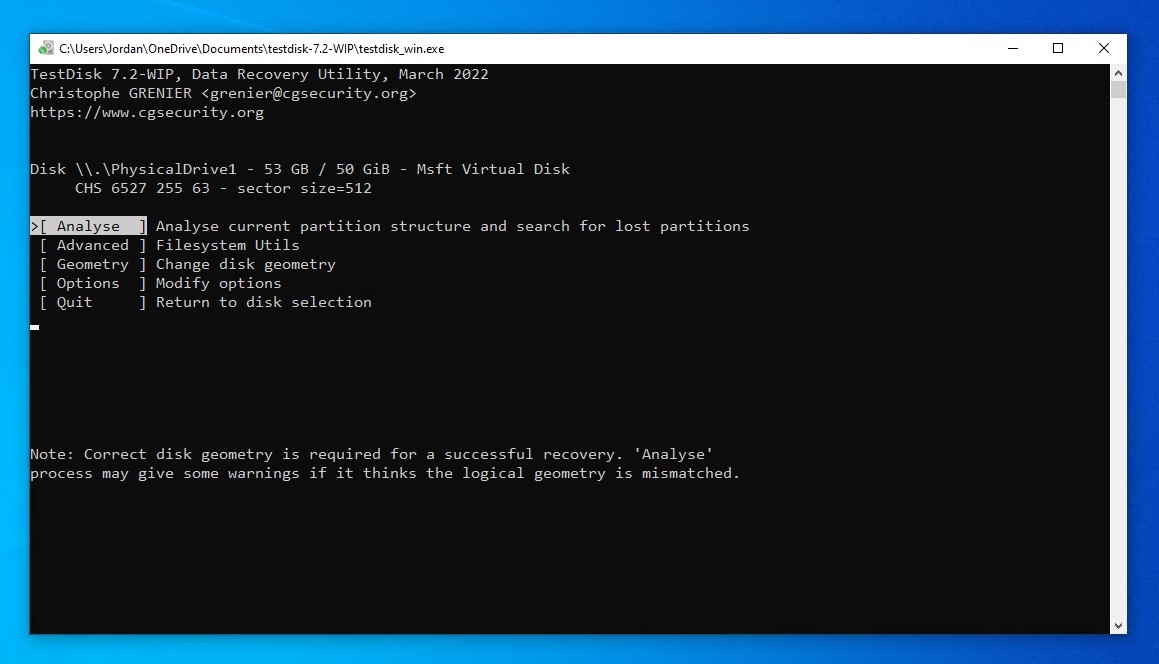
- Press Enter again to start a Quick Search.
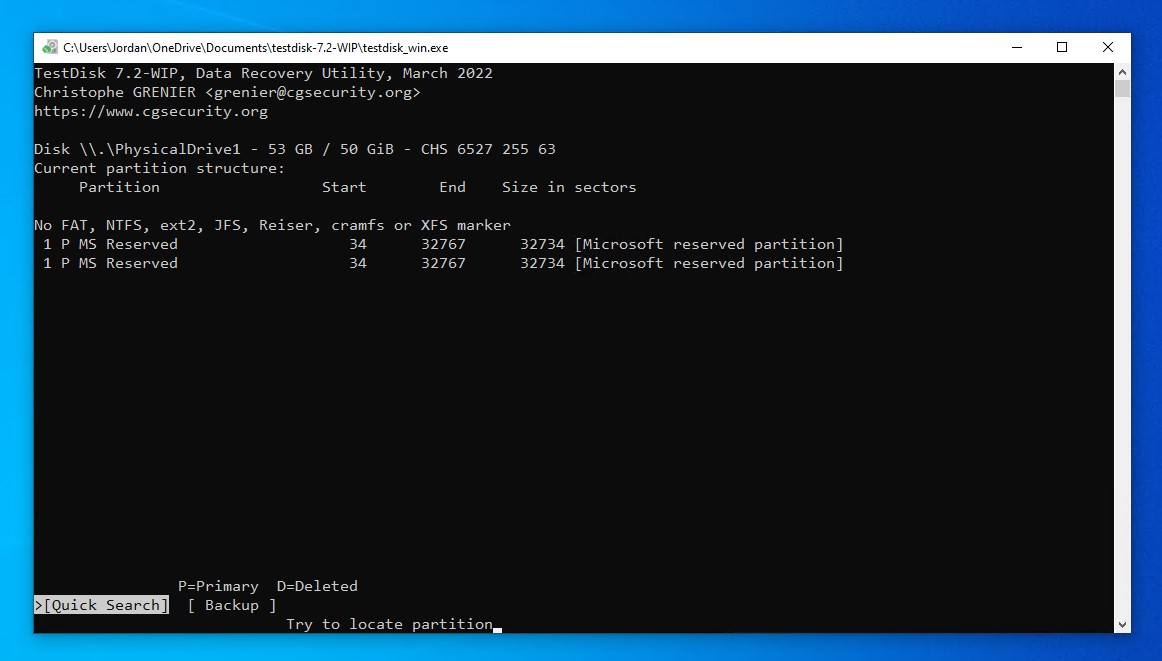
- Press Enter on the found partition.
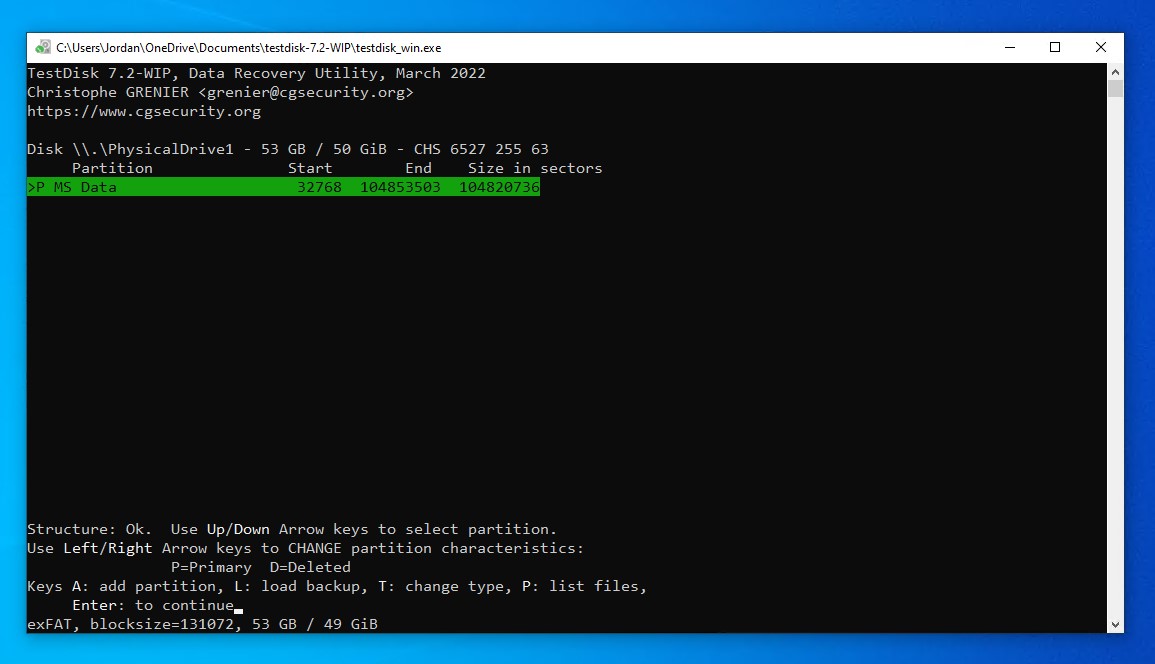
- Move to the Write option, then press Enter. If nothing was found, you can perform a Deeper Search instead.
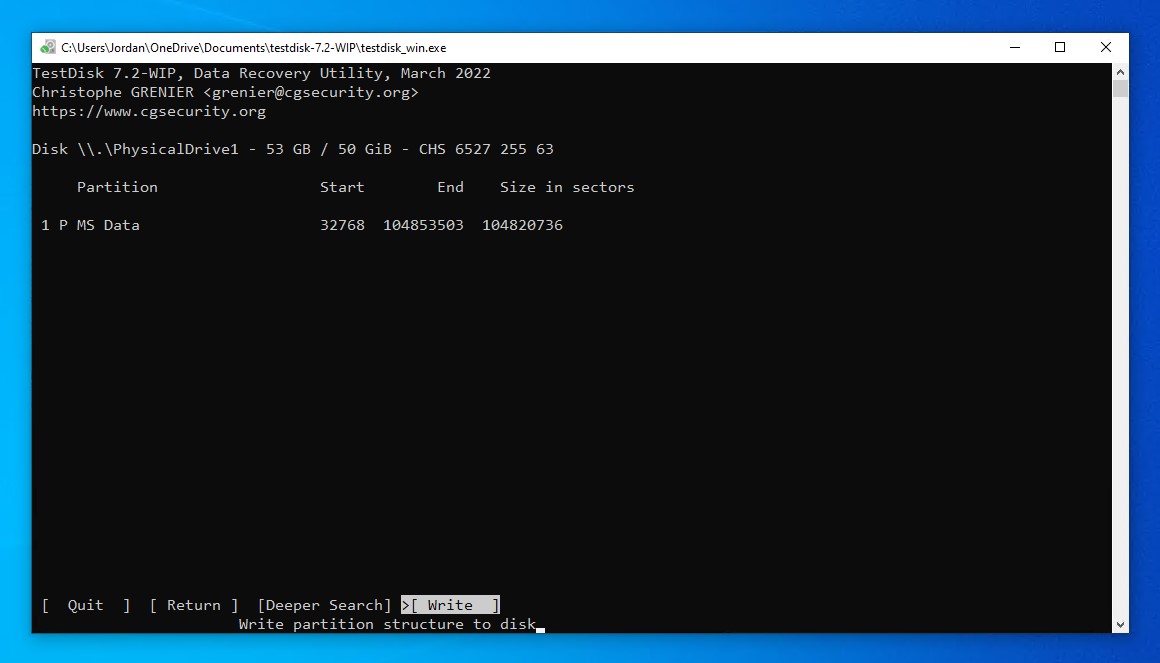
- Press Y to confirm the action. Restart your computer to confirm the changes.
Recover Using a Data Recovery Service
Data recovery software has its limitations. It only relies on its own algorithms to find your data. In more extreme situations, it can usually fall short. If data recovery software isn’t quite cutting it for you, using a data recovery service is your next step.
A professional data recovery service employs the talents of data recovery specialists. In a controlled environment, your drive is scanned using industry-grade equipment to find and recover your data. If you want the best chance of recovering your data, relying on a professional to take care of it for you is your best option.
How to Create a Low-Level Backup of FAT File System
Creating a low-level backup of your FAT file system preserves its current state. Therefore, it’s beneficial to do before you perform recovery to ensure you have a backup that you can use to recover lost data.
To perform a low-level backup, you will need to create a bootable USB containing Ubuntu Linux first. Once your USB is prepared, follow these steps:
- Insert the USB to the computer while it’s powered down.
- Boot from USB into the Linux environment.
- Press Enter on Try or Install Ubuntu.
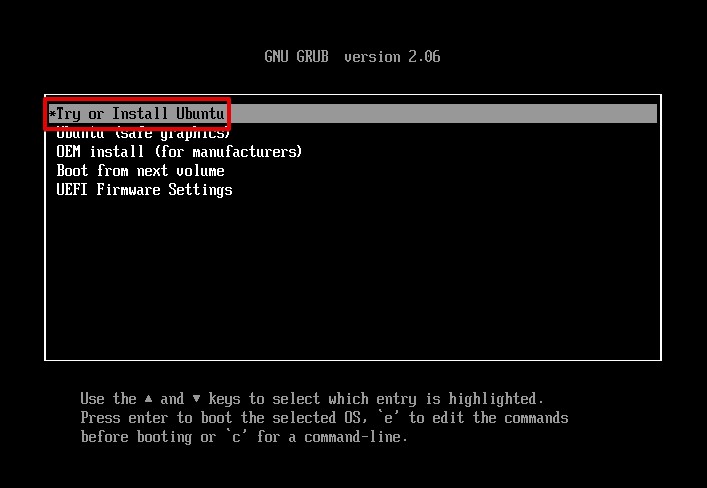
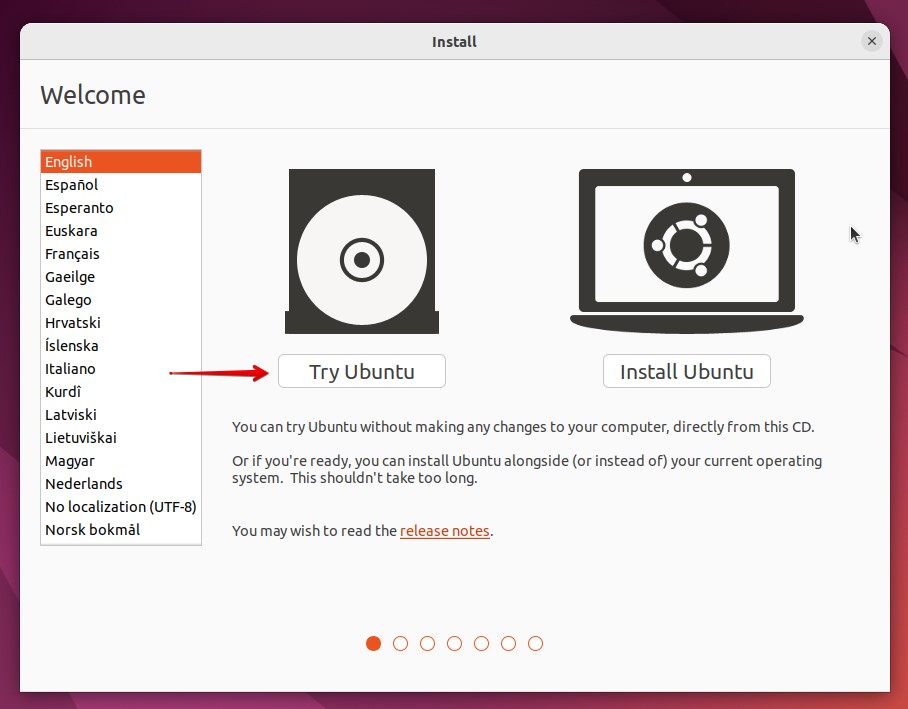
- Click Try Ubuntu.
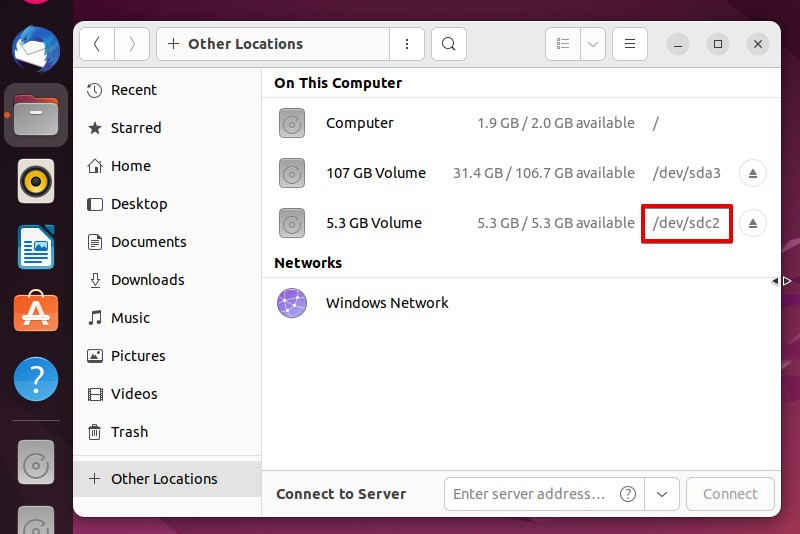
- Click Files, then Other Locations. Make note of the identifier for your FAT partition.
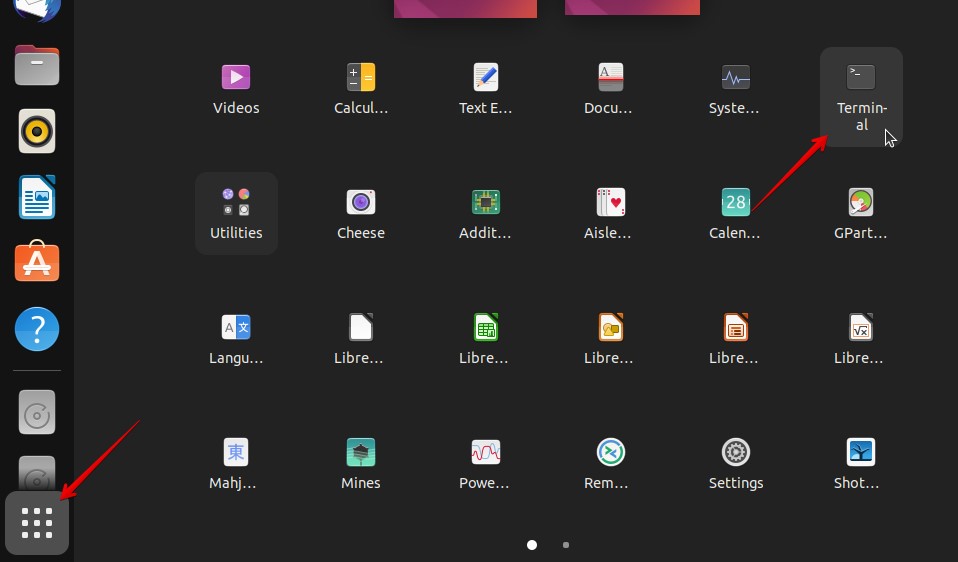
- Click the Show Applications to view all the apps included with Ubuntu, then open Terminal.
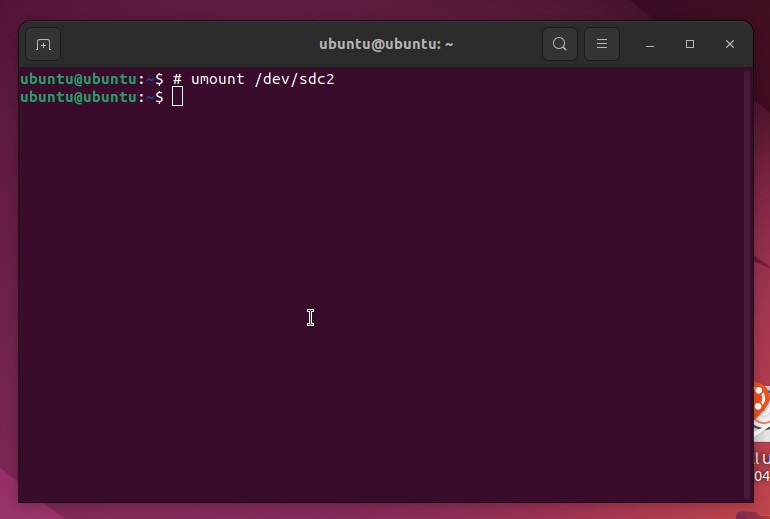
- Type sudo umount /dev/sdc2. Replace /dev/sdc2 with your own disk’s identifier. Press Enter. This will unmount the disk.
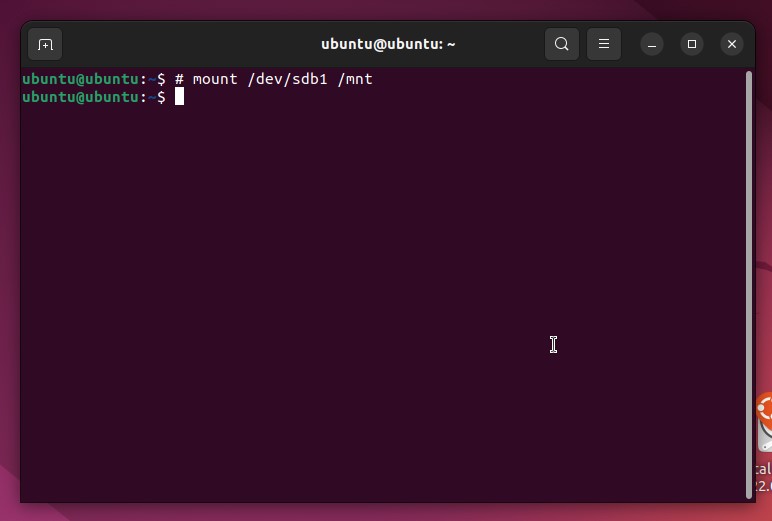
- If necessary, mount the disk you want to store the backup on. Type sudo mount /dev/sdb1 /mnt. Replace /dev/sdb1 with the path of the disk you’re using for output. Press Enter.
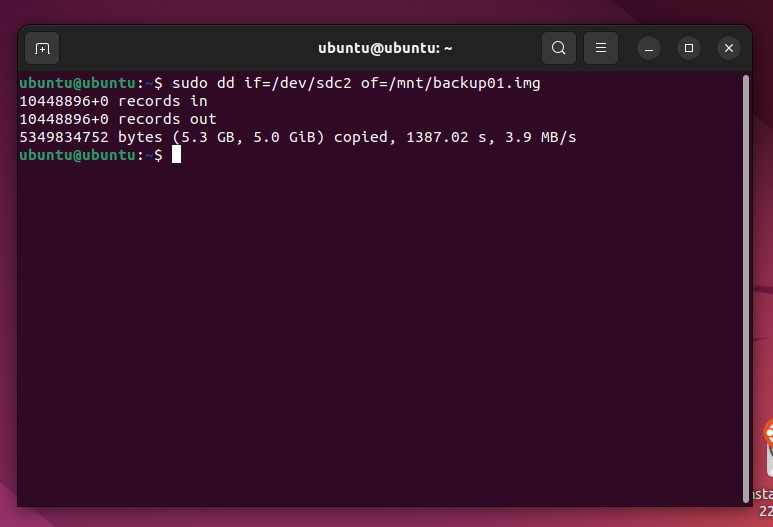
- Type sudo dd if=/dev/sdc2 of=/mnt/backup01.img. Replace /mnt/backup01.img with your own output path and file name.
How Do I Prevent Data Loss on FAT File System
The best way to prevent data loss is to protect your data. A simple backup utility such as File History, which is included with Windows, does an excellent job at taking regular snapshots of your data. In the event that some of your data is lost, you can restore a backup copy using File History.
However, you can also make use of Disk Drill here too. It includes a Data Protection feature that actively protects your data in the event of data loss. Take a look at how you can use it using the below instructions:
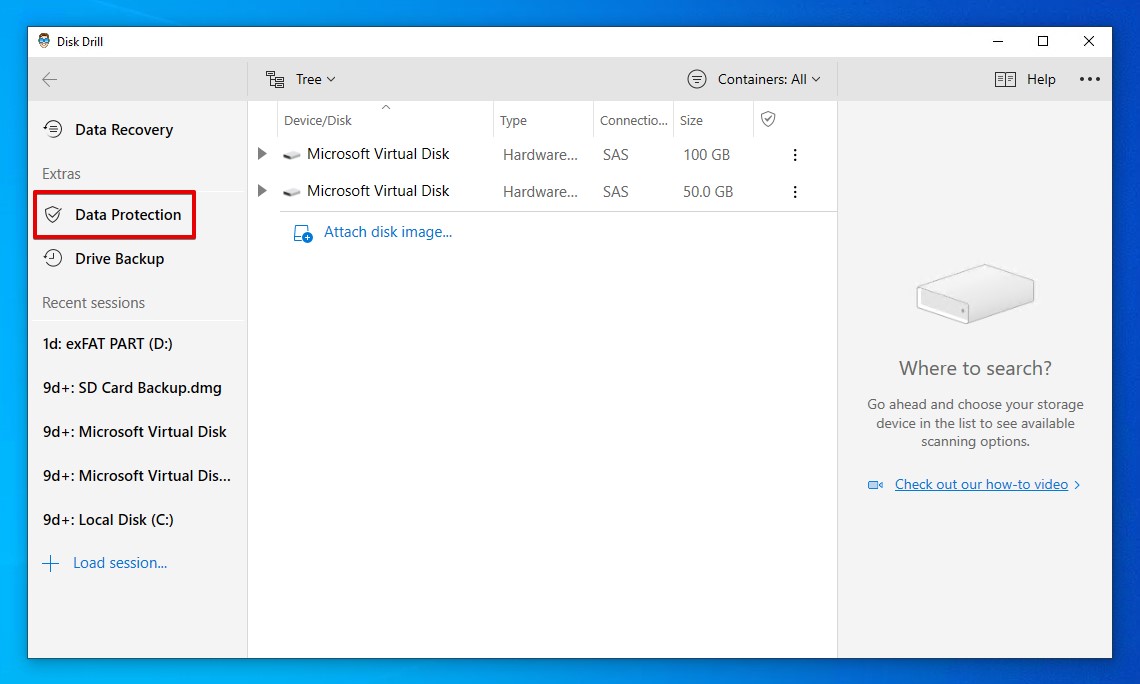
- Click Data Protection. If asked to start the service, click Yes.
- Turn the Recovery Vault on by clicking the slider. By default, Disk Drill protects Users and Documents and Settings when enabled.
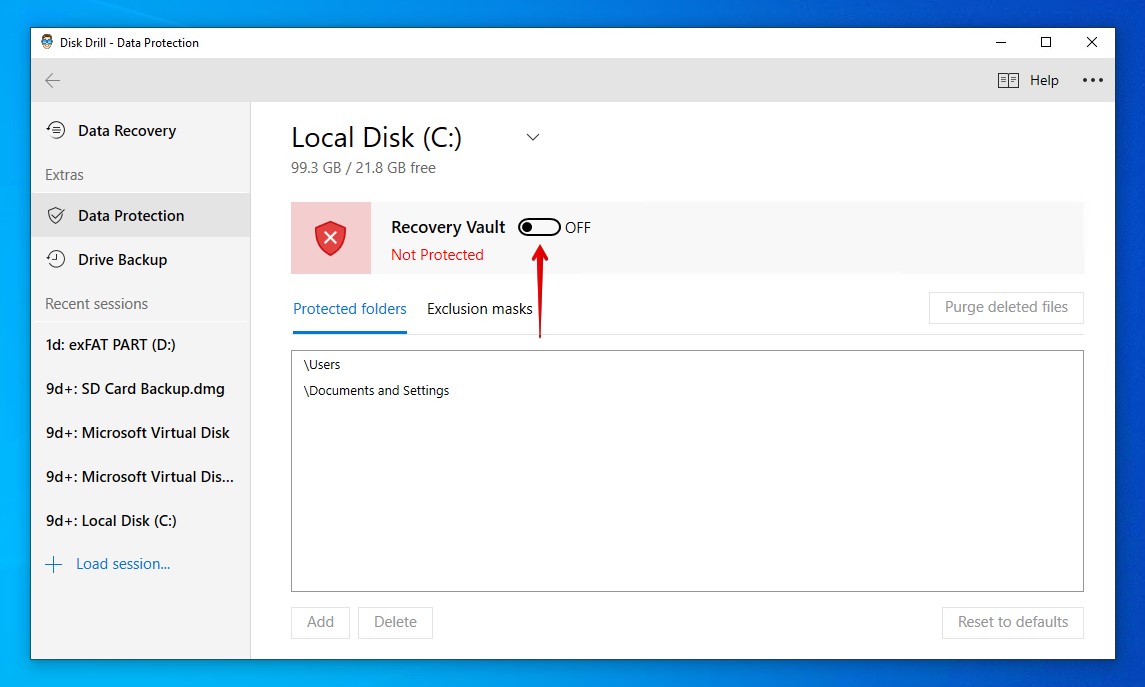
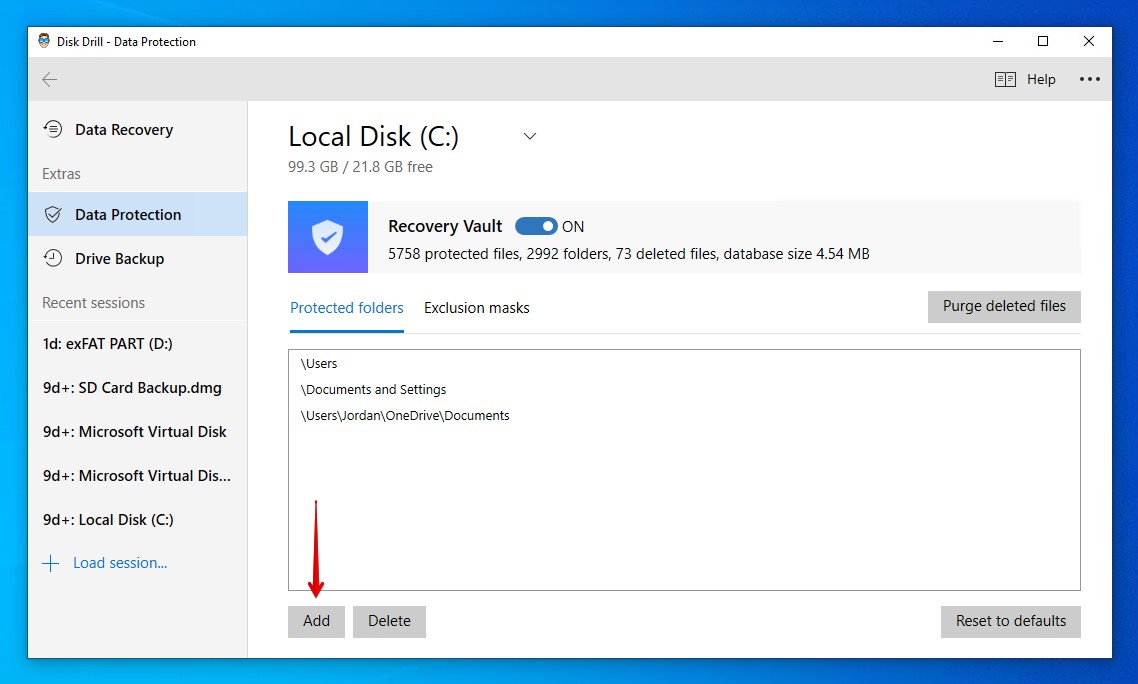
- Click Add to add directories that you’d like to keep protected.
Alternatively, Guaranteed Recovery (GR) is an option for Macs. If enabled, it keeps a copy of any file sent to a specified folder, such as the Trash.
Conclusion
Although variations of the FAT file system are considered outdated now compared to more modern file systems, it’s still largely possible to perform data recovery on them. However, data recovery isn’t always possible. Instead, make sure you implement a reliable backup schedule to retain a copy of your important data at all times.
FAQ
You can recover a FAT file using Disk Drill. Follow these steps to complete FAT recovery:
- Download and install Disk Drill.
- Select the FAT drive or partition. Click Search for lost data.
- Click Review found items.
- Mark the files you want to recover. Click Recover.
- Choose where you want to store the recovered files. Click OK.
The first character of the directory entry for the file is deleted. In the FAT, the sectors where the file resides is marked as available. However, since only the first character is deleted, recovery can be performed using the remainder of the information.
If you had File History or Backup and Restore enabled at the time of data loss, you can restore a copy of your deleted files directly from the backup. If there is no backup of your data, you will need to use a data recovery tool.


