Whether it happened accidentally, someone else did it, or you formatted on purpose before realizing you needed those files, you’ll need to know how to recover files from a formatted hard drive.
The good news is that formatted doesn’t always mean gone for good. There’s a decent chance that you can still recover data from a hard disk after formatting, and this article will guide you through the process step by step, whether you’re using Windows or Mac (the process is similar but with some key platform-specific differences – different file systems, different built-in backup tools, and so on).
What Does Formatting Do to Your Files?
Let’s take a minute to understand what exactly formatting your hard drive does. It’s actually pretty similar whether you’re on Windows or Mac.
Think of your hard drive like a book: files are the words on the pages, and the file system is the table of contents. Formatting removes that table, not the content itself. Your computer can’t find the data anymore, but it’s still there.
That’s why recovery is often possible after formatting with reliable hard drive data recovery software, as long as those pages haven’t been overwritten yet.
Both Windows and macOS handle this process similarly at the basic level. The actual data remains untouched on the physical sectors of the disk until new files are written to those same spots. Where Windows and macOS differ is in their more thorough formatting options. Windows offers a “full format” option that writes zeros to every sector of the disk. macOS goes a step further by providing several “secure” format options (but only for traditional spinning drives):
- A “basic” secure erase option writes random data once and zeros once across the entire disk.
- A “3-pass” option (which meets US Department of Energy standards) writes random data twice, followed by known data once.
- The most secure “7-pass” option repeatedly writes patterns of zeros, ones, and random data across the entire disk.
In practice, all more thorough formatting options – from Windows zeroing to macOS 7-pass overwriting – prevent the recovery of formatted data from a hard drive. However, standard formatting methods don’t. So, unless you remember manually choosing to perform a full or secure format, your chances of success should be good.
Formatted Hard Drive Recovery Without Backups
Without any backups, your recovery success depends on three key factors: the selected formatting method as discussed above, the reliability of the hard drive data recovery solutions you choose to apply, and what happens immediately after formatting, namely:
- Write operations: Every new file you save to a formatted drive potentially overwrites your old data. Even installing recovery software on the same drive could destroy the very files you’re trying to recover. This is why the first rule of data recovery is to stop using the drive immediately after realizing you need to recover files from it.
- TRIM command execution: Another factor that can stand in the way of successful data recovery is TRIM, a performance-enhancing command that can be issued by the operating system to the SSD controller in order to proactively clear out unused storage blocks for new data. Both Windows and macOS automatically use TRIM with compatible SSDs, though its implementation can vary slightly between systems and drive configurations. Once storage blocks are cleared out by TRIM, the files that were on them become permanently irrecoverable, unlike on traditional mechanical hard drives, where data remains physically present until overwritten.
So what’s the best approach to retrieve lost data after formatting? For most people, specialized data recovery software is the only practical solution for recovering formatted drives on Windows and Mac computers without backups.
How to Recover Data From a Formatted Hard Drive Using Disk Drill
Disk Drill is an excellent option when looking for an answer as to how to recover a formatted hard drive. There is a free version available to download, so you can try the tool and see what it can do for you.
Before rushing to scan your drive, however, consider creating a disk image first. With it, you can run multiple recovery attempts without worrying about causing additional data loss. One data recovery software that can deliver great results on both platforms is Disk Drill. It supports all major file systems (NTFS, FAT32, exFAT, HFS+, APFS), can recover over 400 file types, and its byte-to-byte backup feature creates a complete copy of your drive, including all data and empty sectors.
What’s also important, especially if you’re not a computer enthusiast or professional, is that Disk Drill for Windows and macOS has the same user-friendly interface that makes the recovery process straightforward.
Here’s how to use Disk Drill to recover files from a formatted hard drive (the screenshots show the macOS version of the software, but the interface and the process are virtually the same on Windows):
- Download the free version of Disk Drill and install it on your Windows or Mac. Avoid downloading to the disk that suffered data loss to prevent overwriting the files you intend to recover.
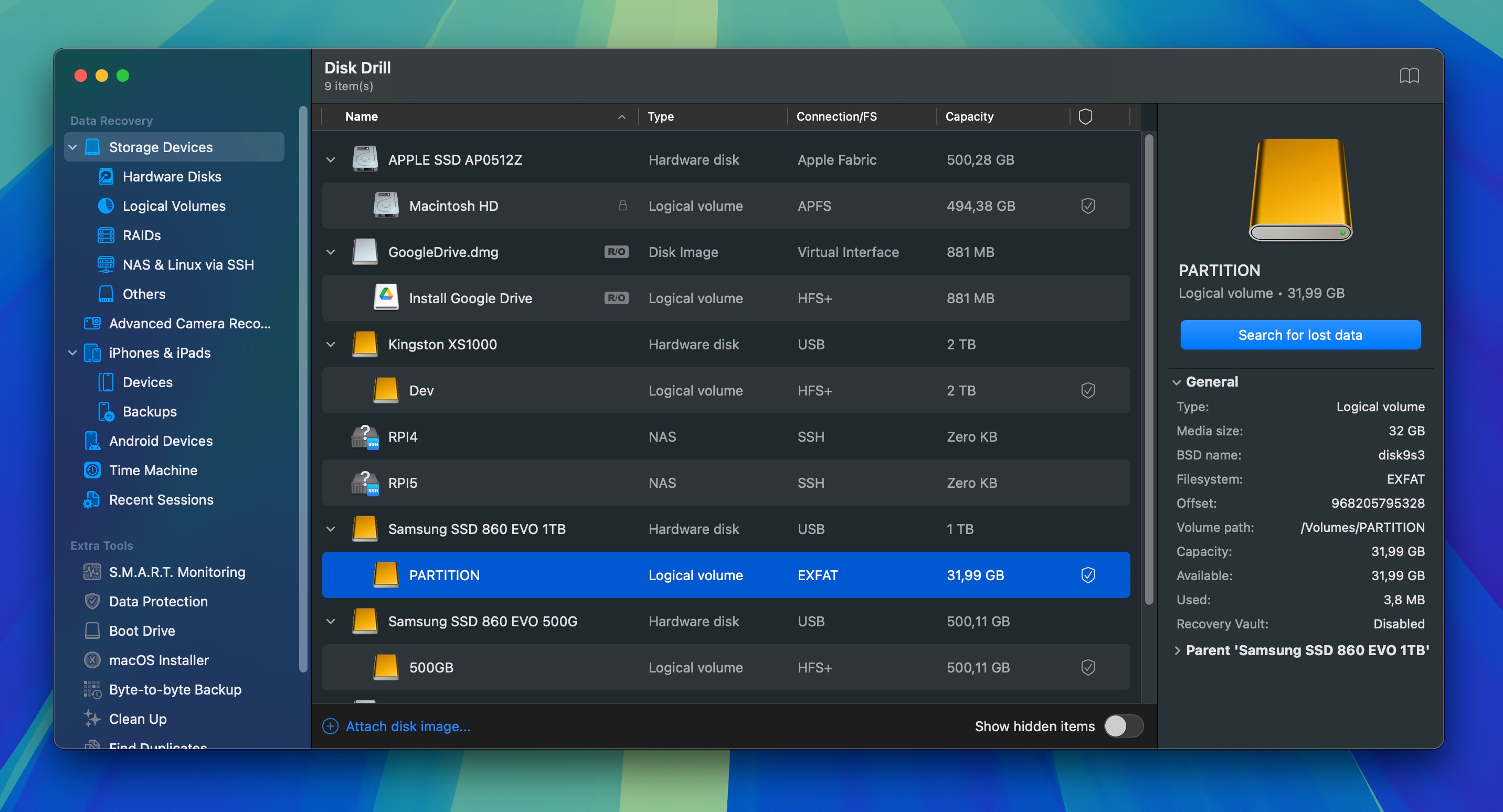
- Attach the formatted drive you wish to recover to your computer first. Once you launch Disk Drill, it will display the drives that it can access.
- Select the formatted hard drive and click on the Search for lost data button to scan it.
- Go through the scan results. You can narrow them down using the available filters or by searching for a specific file using the search bar in the top-right corner. You can also preview many file formats in Disk Drill just by clicking on them.
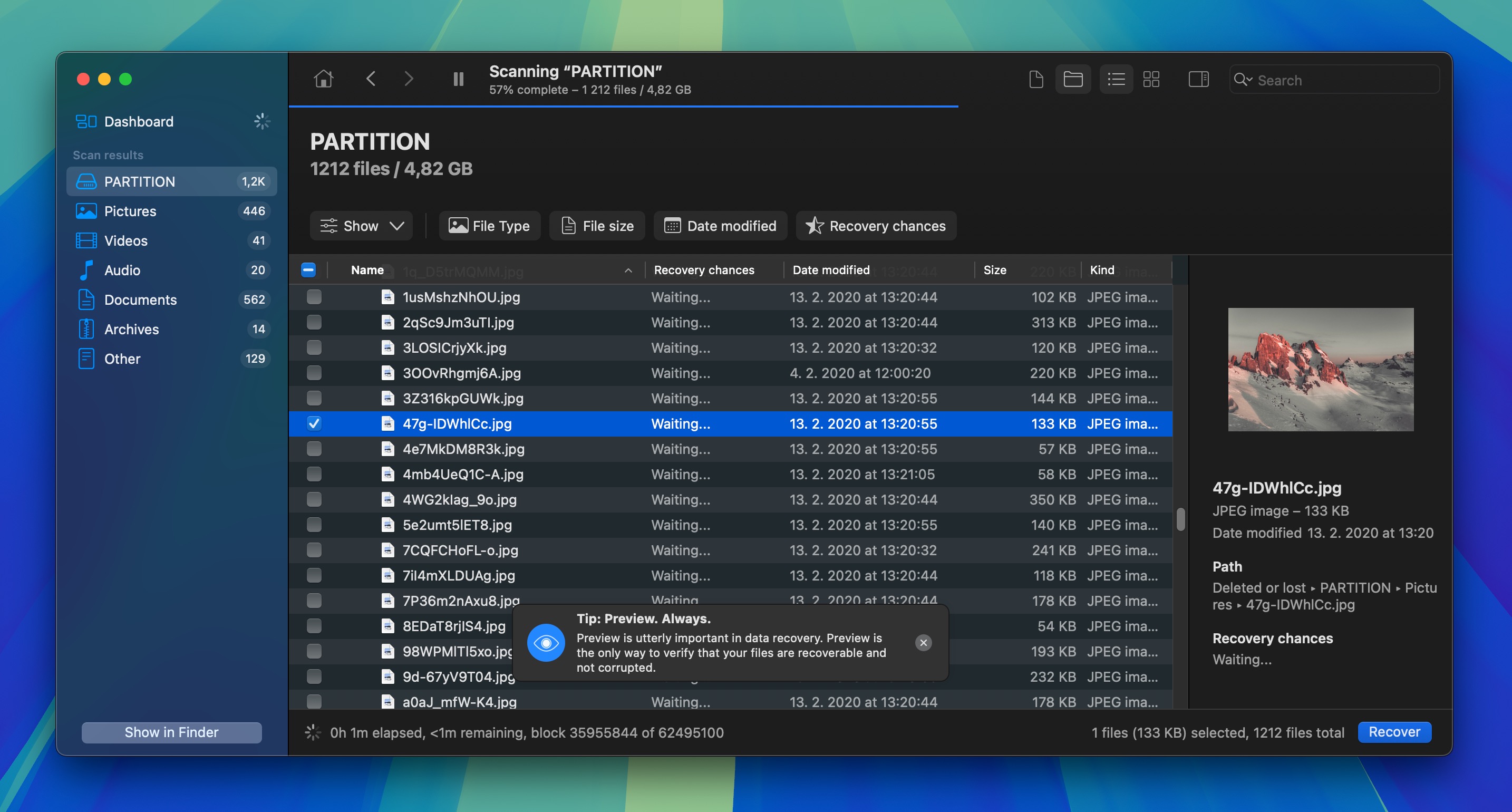
- Choose the files that you want to recover from the potentially recoverable files that are displayed by Disk Drill and click the Recover button. You will be asked to select a suitable recovery destination for the selected files (one that’s different than the formatted hard drive).
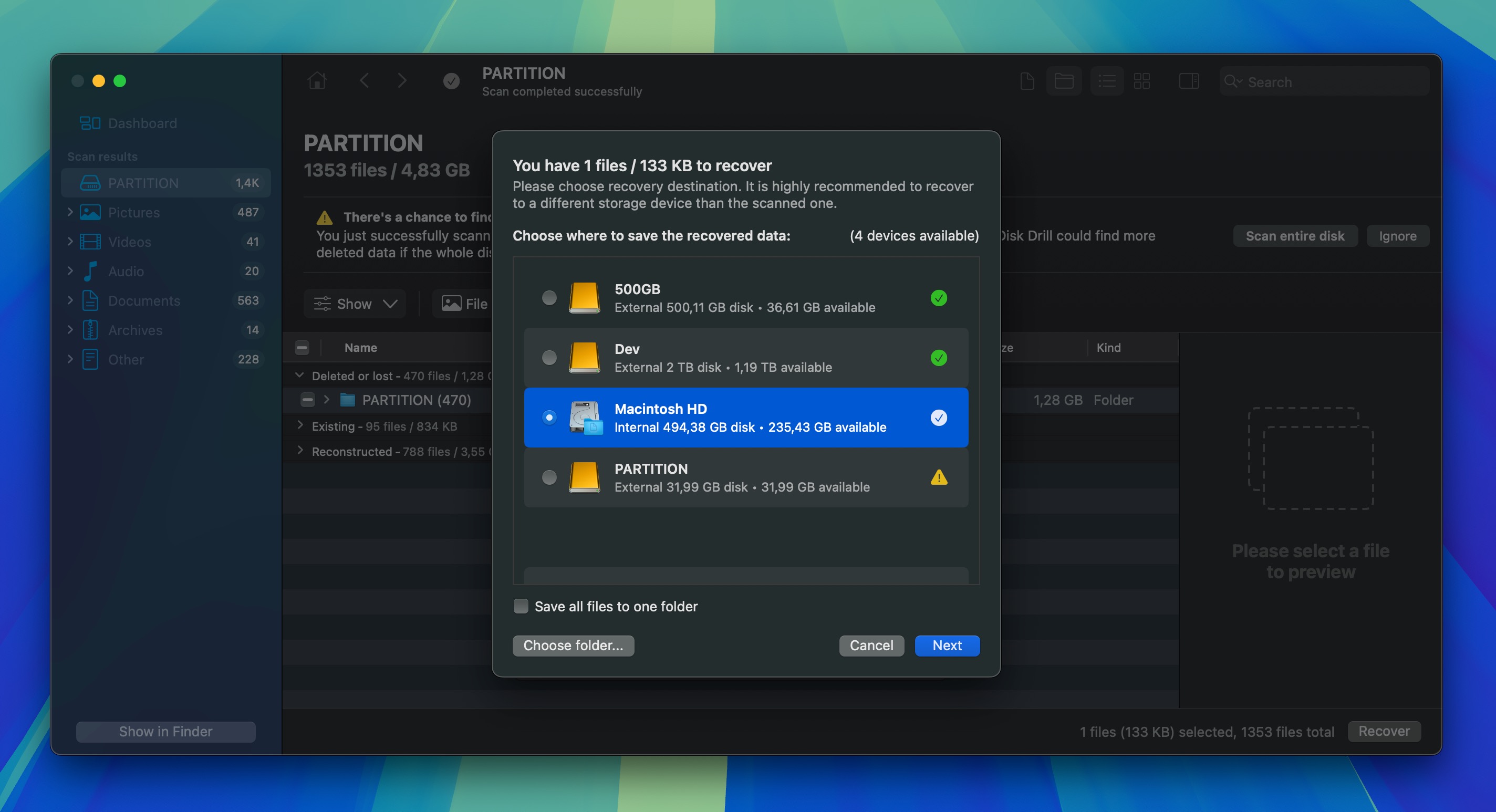
Perhaps the biggest difference between Disk Drill for macOS and Windows is that the Windows version can recover up to 100 MB of data for free, but the Mac version can’t recover files without purchasing the Pro version. But there’s good news for users on both platforms – both versions allow you to preview an unlimited number of files before recovery, so you can verify exactly what can be recovered and decide if it’s worth upgrading to the full version. For light deletions, the free limit can even deliver a complete, start-to-finish recovery.
Recover Data from a Formatted Hard Disk With Backups
If you’ve been diligent about backing up your data, then you should be able to recover data from a formatted hard drive with ease even if you’ve already overwritten the drive with new data.
Both Windows and Mac can back up their data in a number of different ways that range from basic manual copies to more sophisticated automated backup solutions. Let’s take a closer look at all of them so that you can recover your data no matter which approach you follow.
Best of all, the same methods that can save you after a disastrous formatting can also protect you from future formatting mistakes if you implement them now.
Method 1: Check for Manual Backups
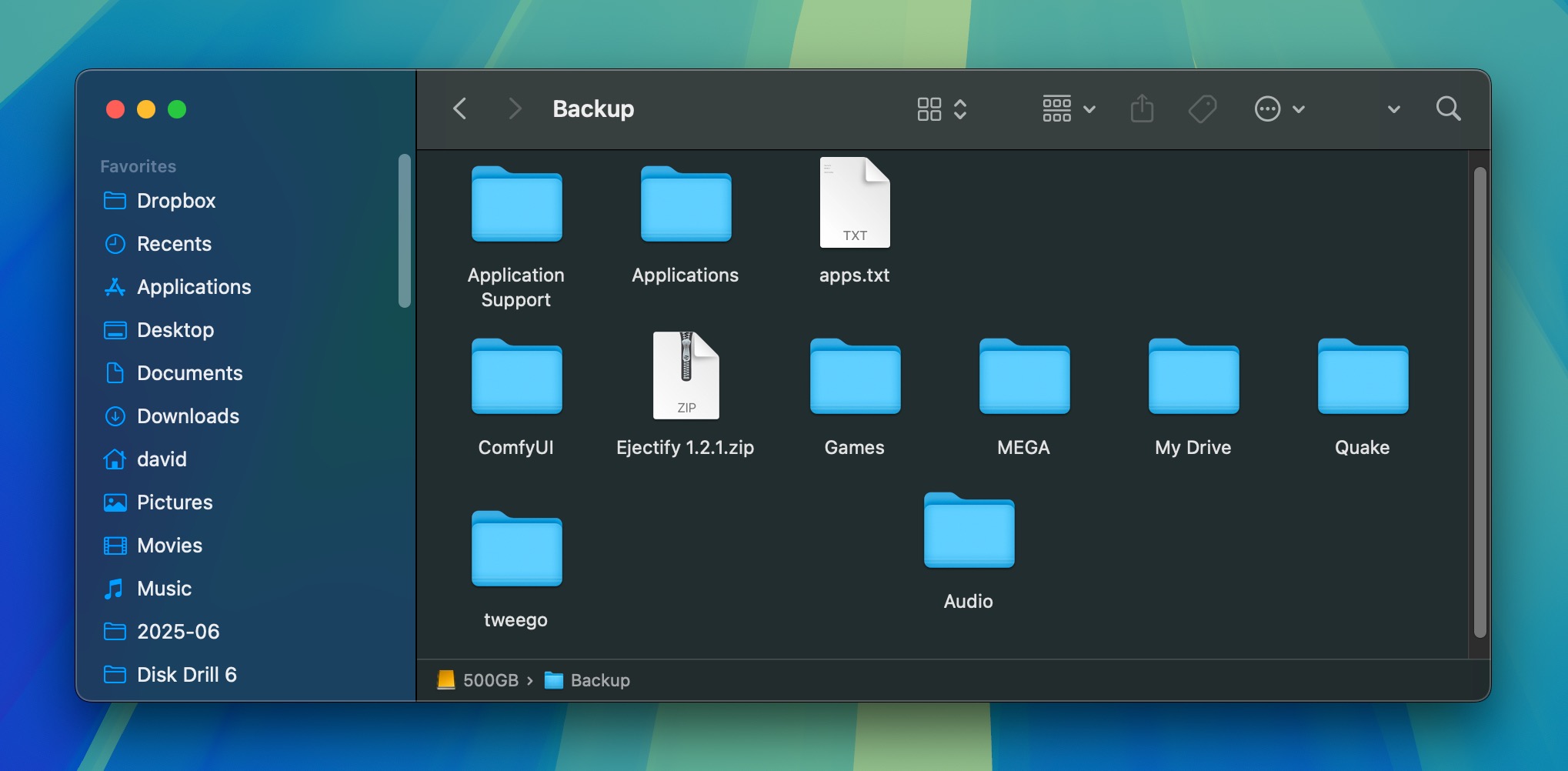
Manual backups are the old-school way to save your data – just copy and paste your precious files from your hard drive to something like a USB stick or an external hard drive. The recovery of lost data from them is also simple:
- On Windows: Open up File Explorer and check any external drives, flash drives, or even secondary partitions where you might’ve saved a copy. If you find any, copy it to the desired destination.
- On Mac: Fire up Finder and go through your external drives, desktop folders, or any cloud storage services synced to your Mac.
If you’re recovering a large number of files, using a file copy tool can save you a lot of time and headaches. On Windows, TeraCopy can help speed up the process and retry files automatically if there’s an error. On Mac, SuperDuper! is a great tool for copying large sets of files reliably and safely.
Method 2: Utilize Automatic Backups
Automatic backup tools like File History on Windows and Time Machine on Mac are the main built-in options for protecting your data, so there’s a good chance that you’ve backed up your files with them. If so, the recovery process could hardly be any easier.
Restore Data with Time Machine Backup
Time Machine is the default backup solution for macOS, and it works by creating regular snapshots of your system and files. If you had Time Machine set up before the hard drive was formatted, then recovery shouldn’t be a problem.
To recover data from a formatted hard drive using your backups:
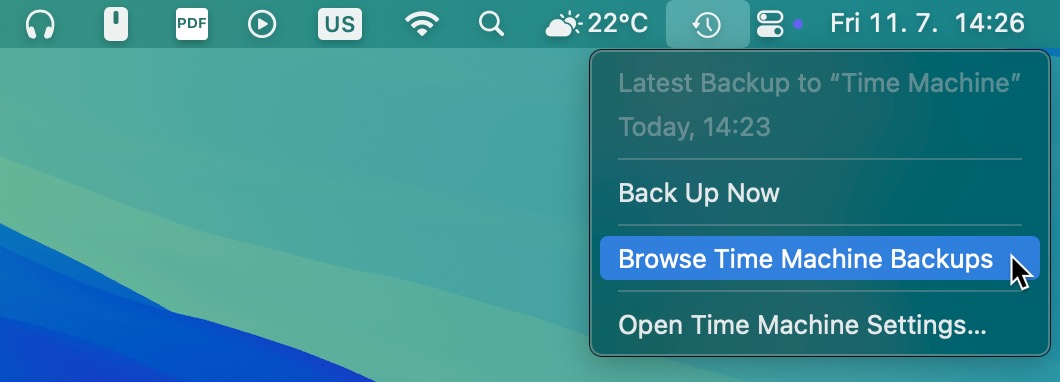
- Access Time Machine by clicking on the Time Machine icon in the menu bar at the top right of your Mac screen.
- Select Browse Time Machine Backups from the drop-down menu to start the recovery process.
- Browse through the backups using the timeline on the right edge of the screen or the arrows to view specific dates and times.
- Find and select the files or folders you need to recover. Click Restore to recover the selected items, which will be returned to their original location on your Mac.
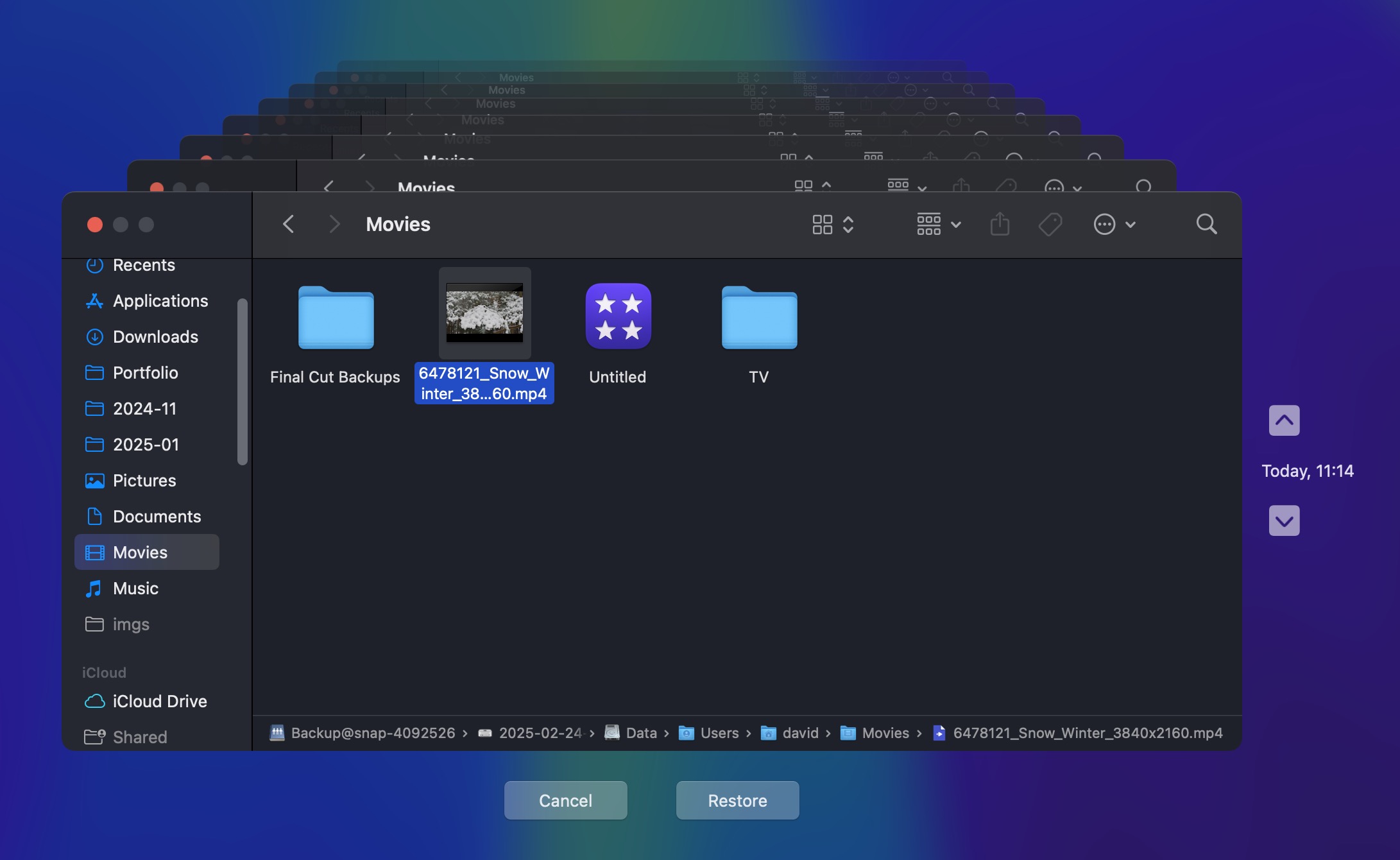
A great thing about Time Machine is that it preserves your folder structure, so restored files will land exactly where they were.
Recover Files Using File History
File History is Microsoft’s answer to Apple’s Time Machine. Even enabled, it saves versions of your files, such as those in Documents, Pictures, Desktop, or Favorites to an external drive or network location, so the formatting of an internal storage device doesn’t affect it.
To recover files from a formatted hard drive using File History:
- Open Windows Settings by clicking on the Start menu and selecting the Settings icon.
- This is where you can access system settings including backup and recovery options.
- Search for File History in the Settings window. This will bring up the option for Restore your files with File History. Click on this option to proceed.
- In the File History window, look for the backups of the formatted drive. You can browse through different time stamps to find the most relevant backup.
- Go through the backups and select the files or folders you wish to recover. File History allows you to choose specific items for recovery.
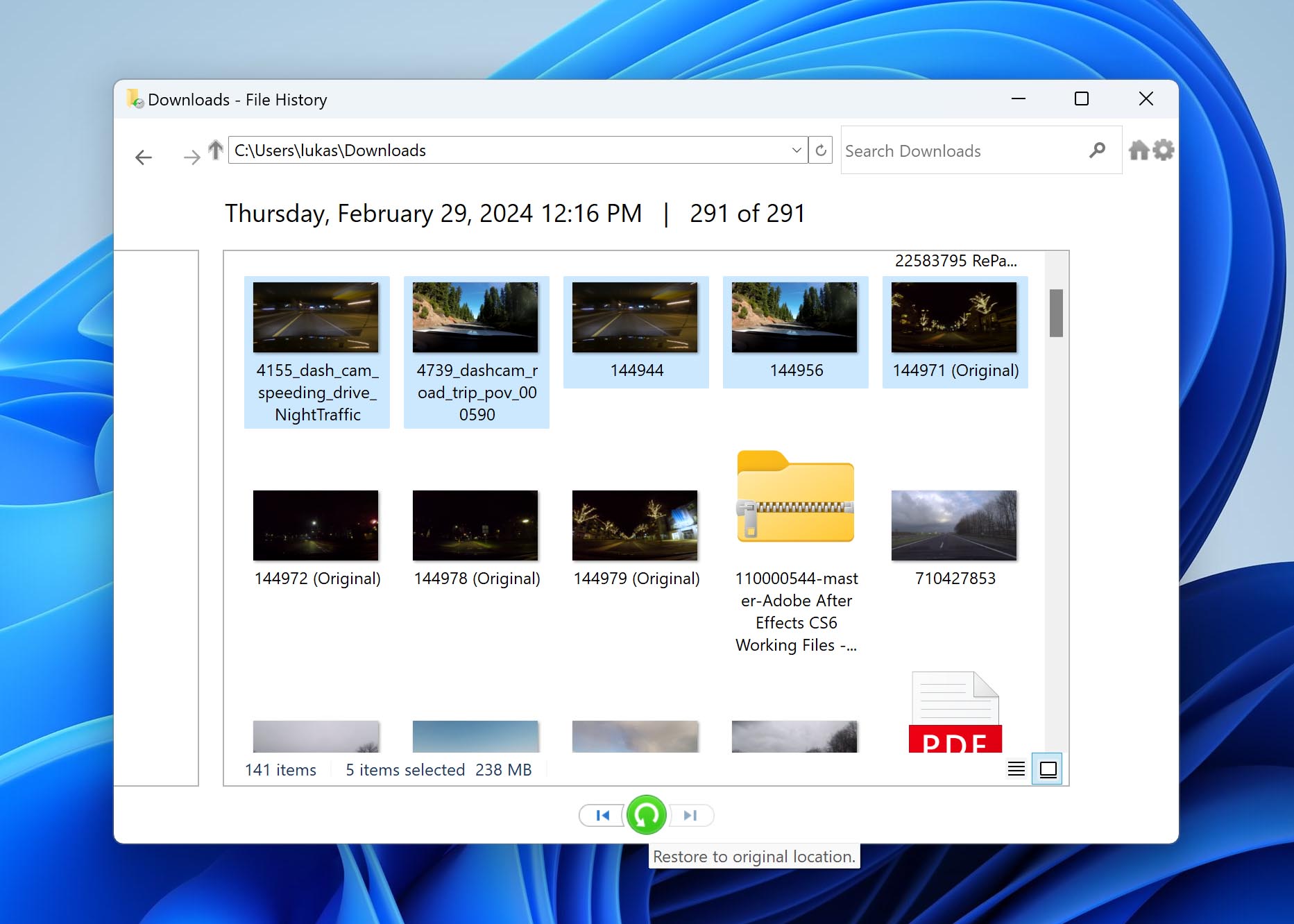
- After selecting the necessary files or folders, click on the green restore button to start recovering the selected data to its original location on your hard drive.
Method 3: Check Your Cloud Backups
Even if you were not intentionally backing up your files before formatting, some of your data may have been saved to the cloud automatically. Services like iCloud, OneDrive, Google Drive, and Dropbox often synchronize important folders such as Documents, Desktop, and Pictures. If cloud sync was enabled, there’s a good chance that at least some of your files are still safely stored online.
iCloud
If you were using a Mac and had iCloud Drive enabled, many of your files – especially those from your Desktop and Documents folders – may have been uploaded automatically.
To check for your files on iCloud:
- Open a web browser and go to icloud.com, then sign in with your Apple ID.
- Click Drive to view synced files.
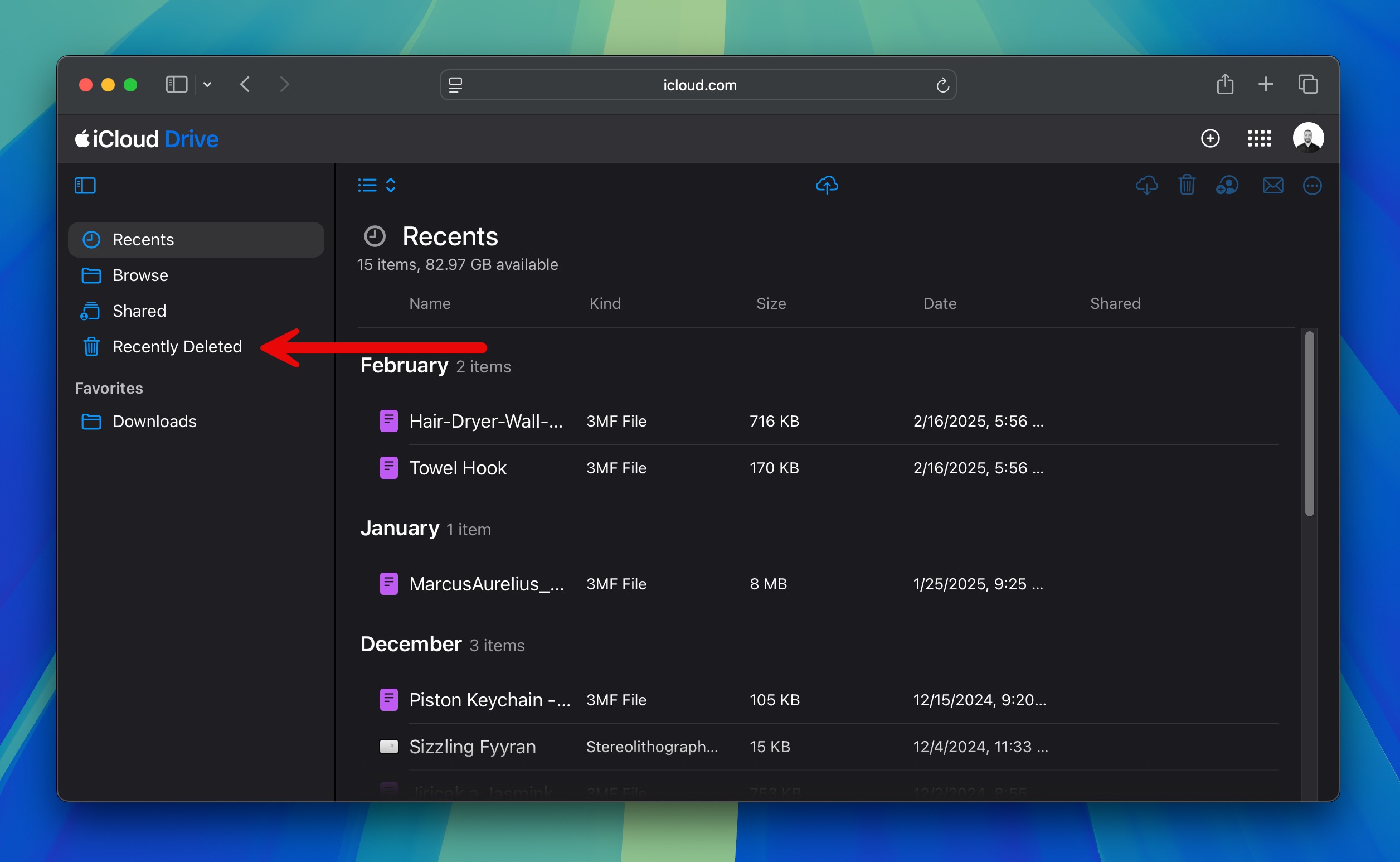
- Browse for the files or folders you need. Use the search bar at the top to find specific items by name.
- Select the files or folders and click the download icon (a cloud with a downward arrow) to save them to your Mac.
- If you recently deleted files, check the Recently Deleted section in iCloud Drive or Photos, as items are kept for 30 days.
A huge advantage of a cloud backup service like iCloud is that you can download your lost files from any device and from virtually any location in the world.
OneDrive
OneDrive is Microsoft’s cloud storage service, and Windows 11 comes with its client pre-installed. If OneDrive was active, it likely synced folders like Documents, Pictures, or Desktop, as well as any content saved in the OneDrive folder itself.
You can recover your OneDrive-backed-up files from the web:
- Visit onedrive.com in a browser and sign in with your Microsoft account.
- Browse the OneDrive interface to locate synced or uploaded files from your formatted drive.
- Select the files or folders you want to recover and click Download to save them to your computer. If the files or folders are located in the Recycle bin, then you need to Restore them instead.
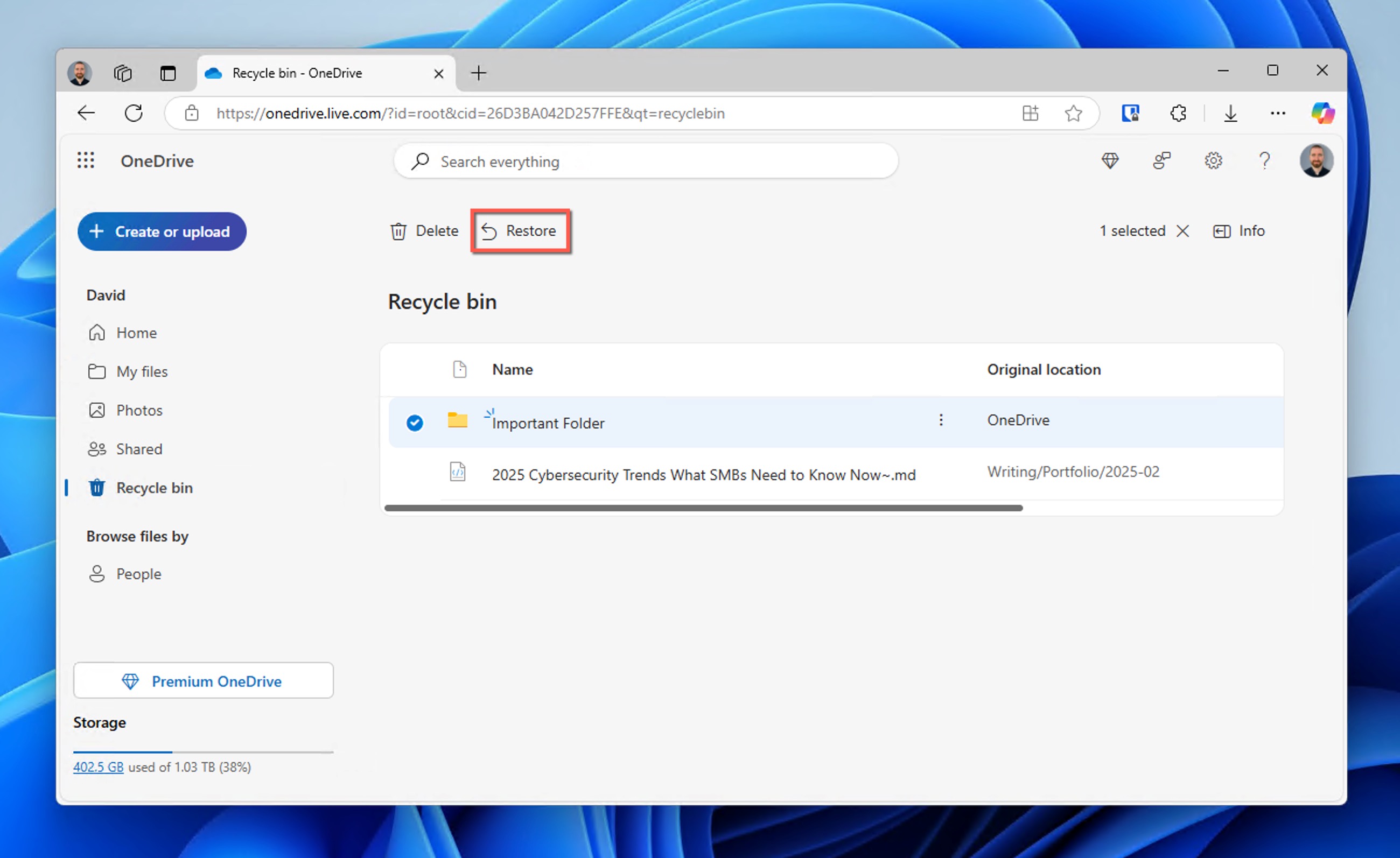
OneDrive maintains folder structures for synced files, but manual uploads may require reorganization. Also, it really helps to have a fast internet connection is key for large downloads.
Other Cloud Storage
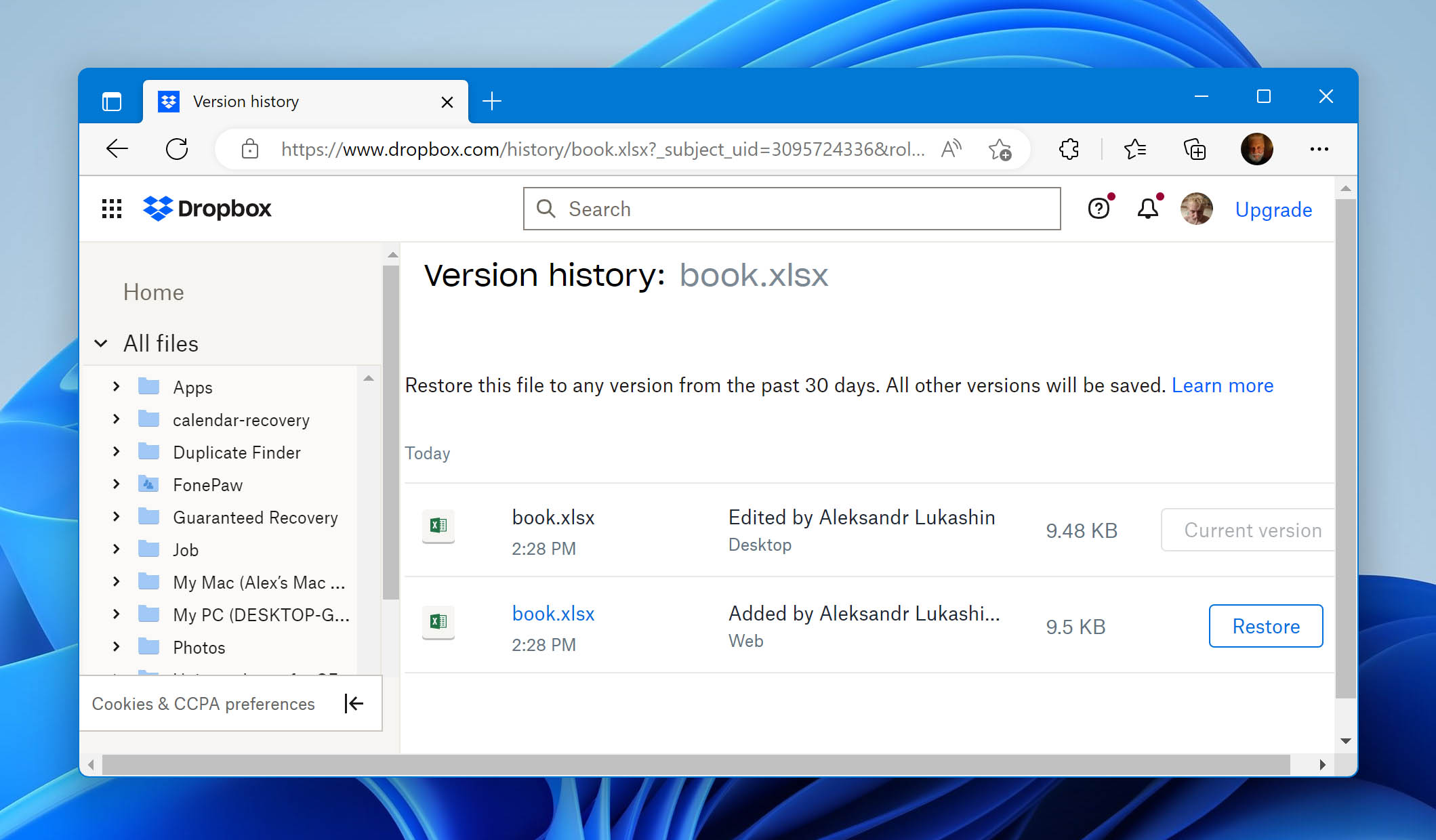
Services like Google Drive and Dropbox are also common for storing files, both through manual uploads and automatic folder syncing.
The recovery process is virtually always the same, but different services offer different data retention policies and recycle bin durations.
With Google Drive, a deleted file is moved to the Trash, where it stays for 30 days before being permanently deleted. During this period, you can restore files directly from the Trash folder. After the 30-day window, the files are permanently removed from your account.
With Dropbox, deleted files are moved to the Deleted Files folder. The duration they remain recoverable depends on your plan: 30 days for Basic, Plus, and Family accounts; 180 days for Professional and Standard plans; and up to 365 days for Advanced, Enterprise, and Education plans. After this period, files are permanently deleted.
Data Recovery Software vs Backups for Formatted Hard Drive Recovery
As we’ve explained, there are two main ways to try getting your data back when a hard drive gets formatted. You can use data recovery software or restore from backups. Both methods have their strengths and weaknesses, and it helps to be aware of them otherwise you might be surprised why you can’t achieve the desired outcome.
Availability
🧰 Data recovery software: One of the biggest advantages of data recovery software is that it’s always available. As long as the drive isn’t physically destroyed, you can download a recovery tool and try to recover your files right away. You don’t need to plan ahead — it’s there when you need it, even in emergencies.
💽 Backups: Backups are only useful if you made them beforehand — and if they’re still working. It’s easy to think you’ll always have a backup ready, but the reality is different. According to Backblaze’s Drive Stats for 2024, the overall lifetime annualized failure rate (AFR) for drives is 1.31%. That’s low, but it’s not zero.
Overwriting
🧰 Data recovery software: Recovering files depends heavily on whether the data was overwritten. Modern SSDs, in particular, complicate things further. Thanks to a technology called TRIM, deleted data gets actively wiped in the background to maintain SSD performance. That means once TRIM has done its job, not even professional recovery tools can bring your files back.
💽 Backups: When properly set up on a different drive or cloud service, backups are immune to overwriting from a formatting event.
Metadata
🧰 Data recovery software: The best formatted hard drive recovery tools like Disk Drill can recover lost files with their original names and folder hierarchies intact, but they can do so only if this information is still available. When it’s no longer available, the recovered files won’t be organized and will have arbitrary names.
💽 Backups: Your entire folder structure and all filenames are brought back exactly as they were when you restore from a backup created using a modern backup solution like Time Machine or File History.
Drive Health Issues
🧰 Data recovery software: If your hard drive needed to be formatted because of serious corruption, hardware issues, or bad sectors, recovery software might struggle. Some files might recover partially, show errors, or be completely unreadable.
💽 Backups: Backups are immune to the original drive’s physical health. If your original disk was failing, your backup (if stored safely somewhere else) remains unaffected.
Why Is Formatting Sometimes Necessary?
It’s easy to see formatting as a destructive operation that causes more harm than good, but that’s not really the case. In reality, formatting is essential for hard drives to be usable. An unformatted hard drive can’t be used to store files because modern operating systems follow certain file storage conventions and can communicate only with storage devices that have a corresponding file system.
The problem is that both modern hard drives and their file systems can be damaged, making formatting a necessary step for making the storage device usable again. Here are the most common reasons why users need to sometimes format their hard drives:
- 🕛 Performance issues: Storage devices, especially older spinning hard drives, may start showing signs of performance degradation over time. Data fragmentation is a common culprit, but it’s not the only one. In many situations, formatting is the simplest and most effective way to restore a slow hard drive to its original performance.
- 💾 File access issues: Modern file systems support complex file access management to ensure that only authorized users can access certain data. But where there’s complexity, there are potential issues. While virtually all file access issues can be solved without formatting, it’s often much quicker to move the affected files elsewhere, format the storage device, and move them back.
- 🗄️ File system change: Not all operating systems and devices support the same file systems, which is why you might need to format your storage device when switching from, let’s say, Windows to macOS or macOS to Linux.
- 🐛 Malware: Modern malware is far more sinister than computer viruses from the 90s. Ransomware can encrypt your entire hard drive without you even noticing, forcing you to format it from scratch to make it usable again.
- 🛑 Data corruption: Data can become corrupted for a number of different reasons. In extreme cases, data corruption may affect even the file system structure itself, requiring you to format the entire hard drive just so you can use it again.
Cases When It Is Impossible to Recover Data from a Formatted HDD
While it’s often possible to recover files from a formatted hard drive, there are a few situations where recovery becomes extremely difficult or even downright impossible. Here’s a closer look at those cases:
- ⚠️ Full Format: Unlike a quick format that just clears the file system metadata, a full format thoroughly overwrites the entire drive with zeros, essentially clearing out all prior data. This process makes recovering any data from the drive virtually impossible. From a professional standpoint, we consider data on a fully formatted drive as unrecoverable using standard recovery tools.
- 🧹 Secure Format: macOS’s Disk Utility offers secure erase options that overwrite data multiple times to prevent recovery. These options include overwriting the disk with zeros and random data. The most secure setting performs a seven-pass erase, writing patterns of zeros, ones, and random data over the entire disk to make recovery impossible not just in practice but also in theory.
- 🔒 Encrypted Drives Without the Decryption Key: If your drive was encrypted with BitLocker on Windows, FileVault on macOS, or any third-party encryption tool, the raw data remains scrambled even if technically recoverable sectors are found. Without the original encryption key or recovery credentials, it’s not possible to restore readable files.
- ⚙️ TRIM-enabled SSDs: Solid-state drives equipped with TRIM support automatically clear unused data blocks soon after files are deleted or a format is performed. Because TRIM physically erases the contents of those storage cells, recovering lost data from a modern SSD (especially post-format) is extremely unlikely. Fortunately, TRIM is predominantly active on internal SSDs connected via SATA or NVMe interfaces. External SSDs connected through USB typically do not support TRIM, which means data recovery might still be possible in those cases.
- 🛠️ Severe Drive Damage: Physical issues like platter scratches (HDDs), NAND chip damage (SSDs), controller failures, or severe logical corruption can make the recovery of formatted drives difficult even for professionals. When hardware damage is involved, specialized cleanroom recovery services, such as those listed in our professional data recovery service guide, may be required, and success is never guaranteed.
How to Check the Status of Your Disk
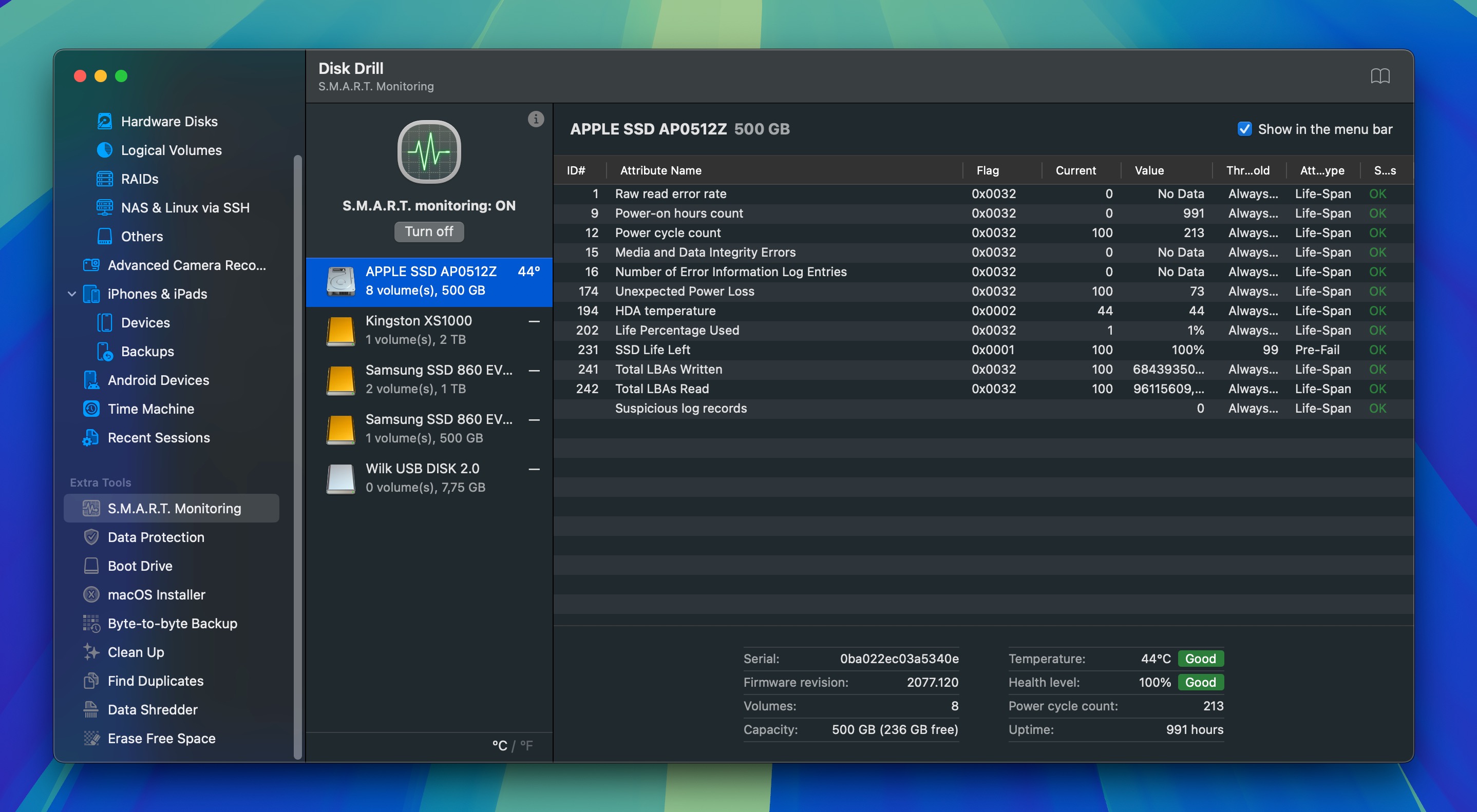
One thing that’s great about modern hard drives is that they are capable of monitoring and reporting their condition through Self-Monitoring, Analysis, and Reporting Technology (S.M.A.R.T.), which is a monitoring system whose primary job is to indicate a possible imminent drive failure.
Other S.M.A.R.T. attributes displayed by Disk Drill include, uptime, power cycle count, temperature, total host writes, reallocated sector count, and many others. Because Disk Drill always evaluates the status of each attribute, you don’t even need to know what they mean to understand how well your hard drive is performing.
Here’s how you can check the status of your disk using Disk Drill:
- Launch Disk Drill.
- Go to S.M.A.R.T. Monitoring in the “Extra tools” panel on the left.
- Turn on S.M.A.R.T. monitoring.
- Look at the health level of the hard drive and its overall S.M.A.R.T. status.
Here you can find more info on how to turn S.M.A.R.T. monitoring ON for external devices.
Conclusion
Sometimes, formatting is the quickest and most effective solution to all kinds of file system issues. The process will, however, leave your hard drive completely empty. If you know how to recover files from a formatted hard drive, you can not only fix file system issues but also regain access to any files lost in the process. In this article, we’ve explained everything you need to know about formatted hard drive recovery, so it’s now up to you to make good use of your newfound skills.
FAQ
If you’ve accidentally formatted a hard disk with important data, then you need to use a data recovery software solution like Disk Drill to scan it and retrieve the lost files. Keep in mind that your data can be recovered only until it becomes overwritten, so act quickly and don’t write any new data to the formatted hard disk.
The first step in recovering data from a formatted hard disk on Mac is to check if you have any backups through Time Machine, iCloud, or manual backups. If you don’t have backups available, then data recovery software like Disk Drill becomes your most effective solution:
- Download and install Disk Drill on your macOS.
- Connect the formatted drive to your Mac computer.
- Launch it and scan the formatted hard disk.
- Click Recover and specify a suitable recovery location.
Recovering data from a formatted external hard drive is just as straightforward as recovering formatted internal hard drives. The trick is to begin the data recovery process before the deleted data become overwritten and use a reliable data recovery software application.
External drives typically aren’t protected by default by internal backup features like Time Machine or File History. Unless you’ve manually backed up your data before formatting the external drive, data recovery software will be your primary option for getting your files back:
- Download and install Disk Drill.
- Connect the formatted external hard drive to your computer.
- Launch Disk Drill and scan the formatted hard drive.
- Select all deleted or lost files from the scan result.
- Click Recover and specify a suitable recovery folder.
We always recommend creating a disk image of your drive and scanning the image instead of the drive itself. This approach is advisable because it minimizes the risk of further data loss or damage to the drive during the scanning process.
If you have access to a Windows computer, then you can recover a formatted hard drive by running the Windows File Recovery tool from the command line:
- Install Windows File Recovery.
- Launch CMD.
- Enter a recovery command in the following format: winfr source-drive: destination-drive: [/switches]
You can learn more about the available recovery modes and switches on Microsoft’s website, which also provides several examples that you can copy & paste.
Recovering data from a formatted hard disk without using software is inherently challenging. The most effective strategy to safeguard against data loss is to have a previously created backup of your important files. If a backup is not available and the data lost is critical, contacting a data recovery lab near you becomes the next viable option. However, it’s important to be aware that professional data recovery services can be costly.


