TOTAL DOWNLOADS
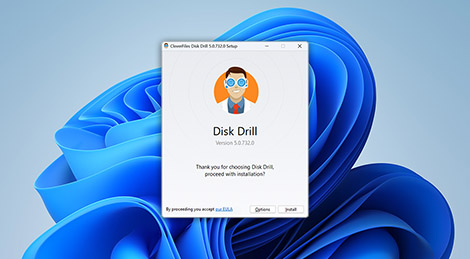
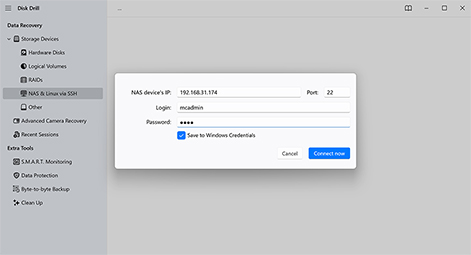
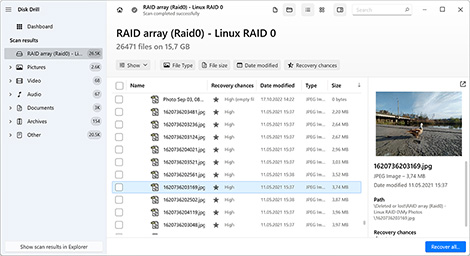
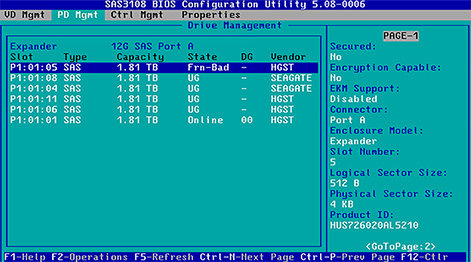
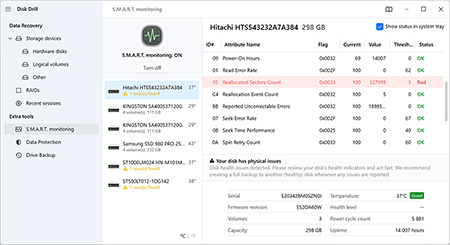
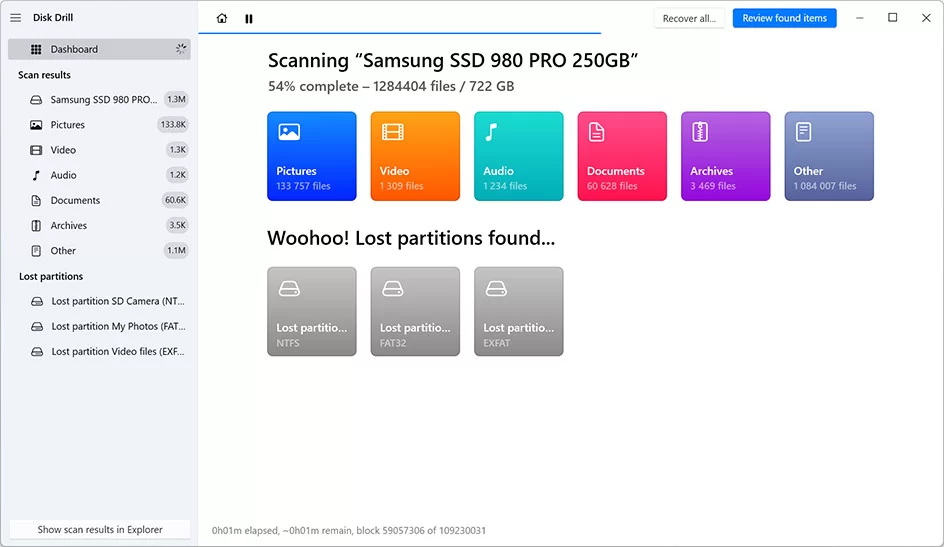
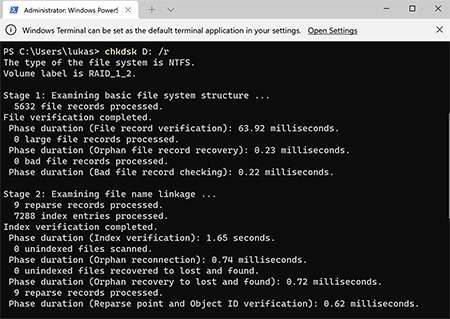
The free version of Disk Drill lets you scan RAID drives and preview recoverable files, even if the RAID array is no longer working as a whole. While Disk Drill doesn’t fully rebuild complex RAID configurations, it can automatically identify and reconstruct certain arrays, especially if RAID metadata is still intact.
You can also scan individual member drives, preview files, assess recovery chances, and even recover some lightweight files on Windows, all without a license.