A week ago, my father deleted an entire folder full of important work documents. He promptly managed to recover about 95% of them from backups, but the remaining 5% (the most recent and important ones) were not backed up. If you’re facing a similar situation and are wondering how to recover a deleted folder from your desktop or any other location, then you’re in the right place because this article describes the same methods I’ve successfully used to recover my father’s missing work documents.
Do’s and Don’ts If You Accidentally Delete an Entire Folder
When you discover that you’ve accidentally deleted an entire folder, there are certain actions you should perform immediately and some you need to avoid to maximize your chances of successful recovery:
✅ DO:
- ⏪ Try the Ctrl + Z shortcut. Windows maintains a history of recent actions, and the universal “undo” command works for file operations just as it does for text editing. If you’ve, for example, very recently deleted a folder in File Explorer, then here’s how to undelete a folder in Windows: open the File Explorer window, navigate to the location where the deletion took place, and press Ctrl+Z. Hopefully, the folder will instantly reappear. If not, move to the next bullet point. Keep in mind that undo history resets when you restart your computer and is session-bounded, so this method only works if you haven’t closed File Explorer or rebooted since the deletion. If the folder doesn’t reappear, move to the next bullet point.
- 🗑️ Check the Recycle Bin. In many situations (see the next section for a detailed explanation), deleted folders are moved to the Recycle Bin. To check if your folder is in the Recycle Bin, simply double-click the Recycle Bin icon on your desktop, look for your folder, right-click it, and select Restore to return it to its original location.
- 💾 Handle SSDs with extra care. If the deleted folder was on an SSD, you’re racing TRIM (called Deallocate on NVMe). This performance-enhancing command marks blocks as free for quicker reuse. Once marked, the drive may physically erase them at any time during garbage collection and that makes recovery essentially impossible. Act fast.
❌ DON’T
- 🚫 Don’t keep using the folder’s parent location. If you can’t find the deleted folder in the Recycle Bin, then it’s most likely been permanently deleted. The good news is that it’s possible to recover permanently deleted folders in Windows, but you must stop writing new data to the drive where the deleted folder was located. Otherwise, you might overwrite the deleted data that still (hopefully) remains physically on the drive.
- 🧑💻 Don’t recover back to or install data recovery software on the same drive/partition. Never install recovery software on the same drive where your deleted folder was located. Doing so could overwrite the very data you’re trying to recover. Instead, install the software on a different drive (like drive D: if your deleted folder was on drive C:). Similarly, when you retrieve deleted folder in Windows, always save the recovered files to a different location.
- ⚙️ Don’t leave scheduled tasks running. Don’t leave scheduled tasks on (backups, indexer tweaks, big updates, defragmentation) that write to the same disk. Any task that causes write operations, which includes moving existing files around, can overwrite your data and make it impossible to get back permanently deleted folder in Windows.
By now, you’ve likely checked your Recycle Bin and discovered your folder isn’t there. Perhaps you used Shift+Delete, exceeded the Recycle Bin’s size limit, or deleted the folder from an external device. Maybe you emptied the Recycle Bin without realizing your important folder was inside. If that’s the case, your next step is to use data recovery software for Windows.
How to Recover Permanently Deleted Folders on Windows PC
Without backups, data recovery software is your only real option for getting back permanently deleted folders. Here’s what you can realistically expect:
- Best-case scenario: you recover complete folders with all files intact.
- Mid-range outcome: you get the files back but lose the folder structure.
- Worst case: the data has been overwritten and nothing can be salvaged.
The only way to find out which situation you’re in is to install recovery software immediately and scan the affected drive.
w/ Disk Drill from @Cleverfiles I was able to recover my music folder (over 100 GB) which I deleted accidentally… Just Thank You !!!
— Moncef (@cesef) January 24, 2019
Follow these steps to recover permanently deleted folders:
- Download Disk Drill for Windows and install it. Don’t forget to never install Disk Drill on the drive where your deleted folders were stored.

- Launch Disk Drill for Windows, select the storage device from which your folder was deleted, and click the Search for lost data button. If you’re scanning a non-system disk, select Universal Scan in the pop-up window that appears.
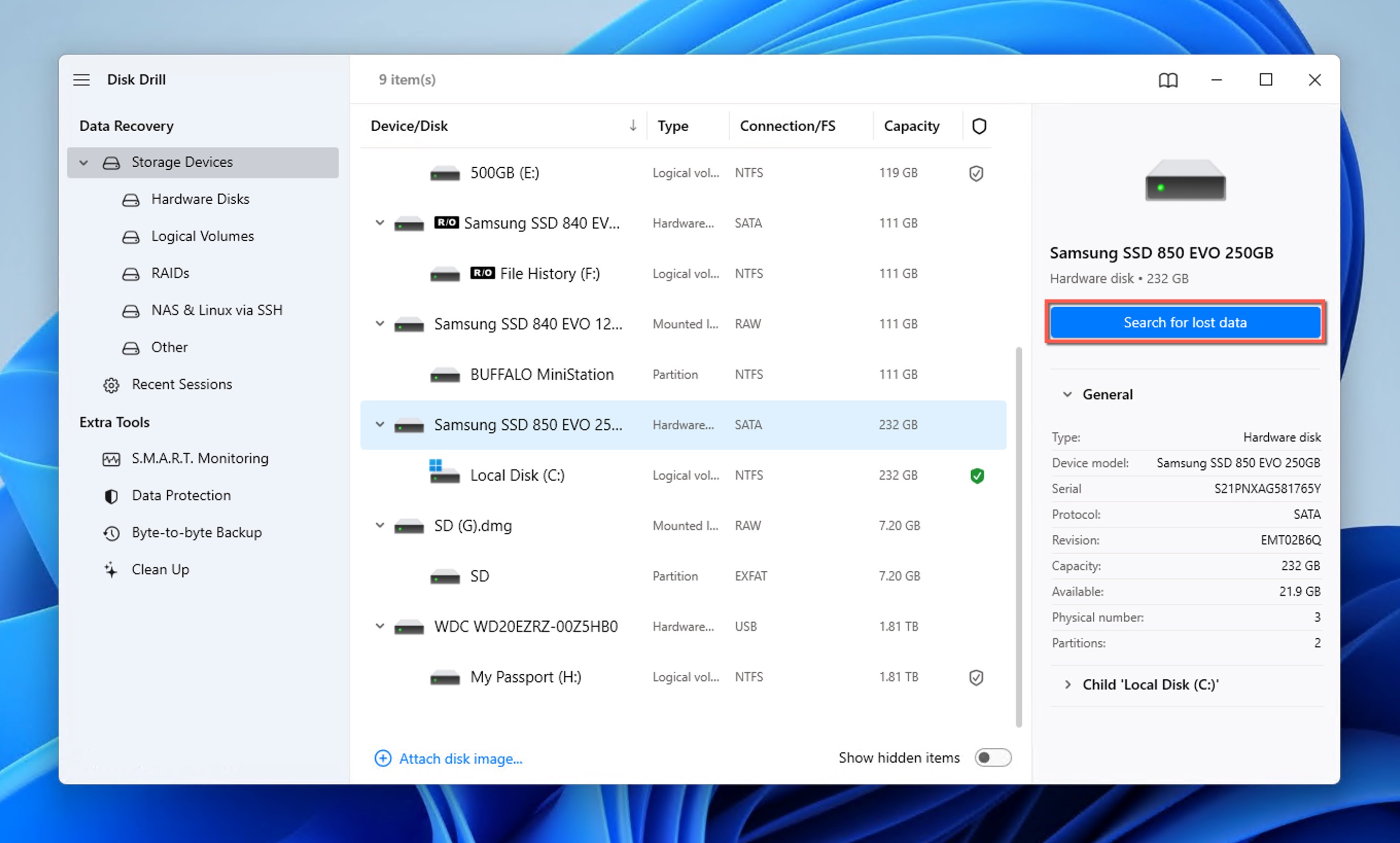
- Wait for Disk Drill to find all recoverable files. The software automatically combines multiple scanning methods to maximize your chances of recovery, and it displays detailed information about its progress so that you can always see how many files have been found and how much time the scan will approximately take. If you don’t want to wait for scanning to finish, you can click Review found items early.
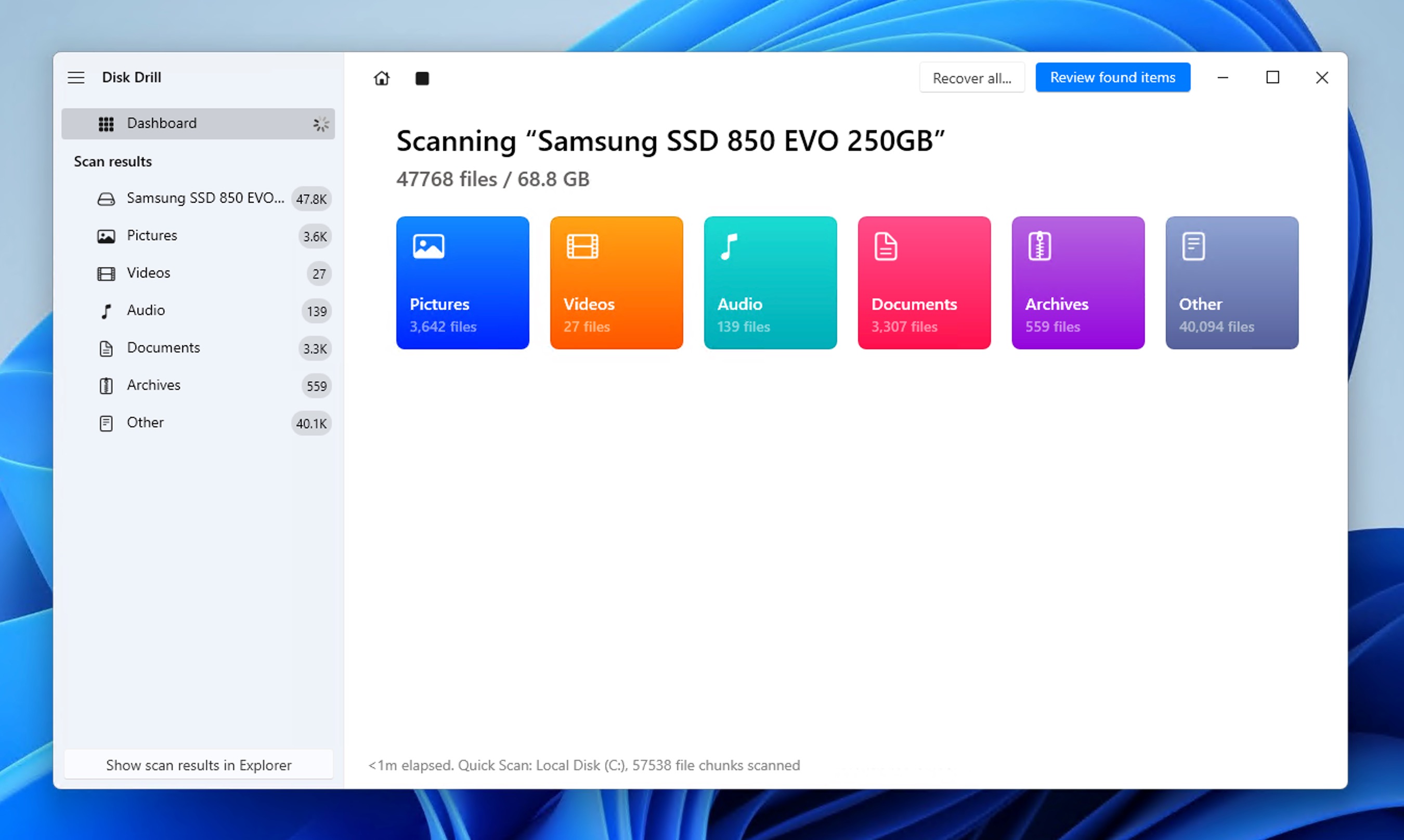
- Select which files you want to recover. You can either recover entire folders or select specific files. Additionally, you can sort the results in a number of different ways and even enable file type filters, which can greatly help if you’re looking for specific file types, such as Word documents or pictures.
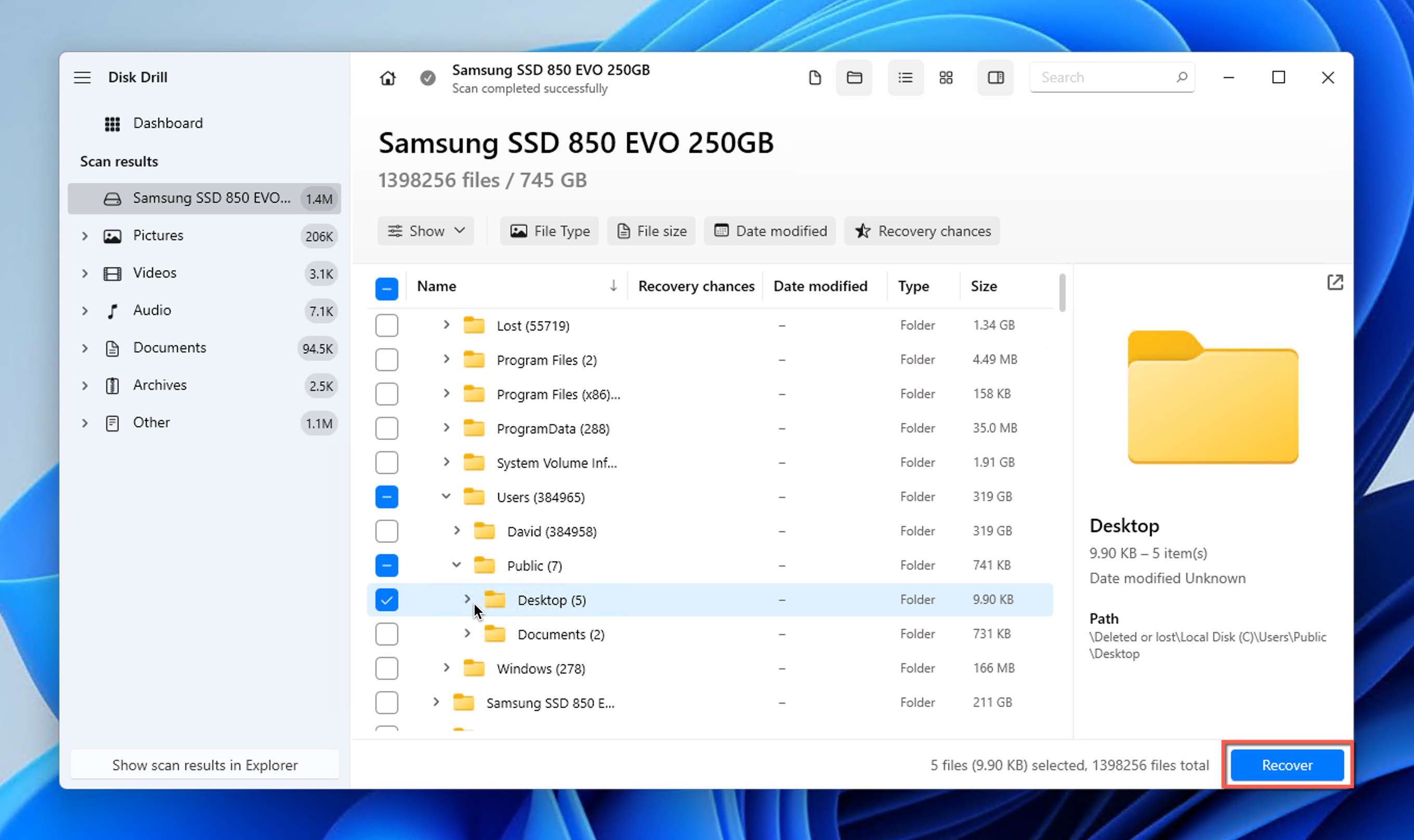
- Begin the recovery process by clicking the Recover button. You will be asked to choose a suitable recovery directory. Again, pick a location on a different storage device than the one where the deleted folder was located.
To keep things simple, we’ve moved the detailed software overview to the end of this guide. However, it is important to explain why we chose this tool. Here is what makes Disk Drill stand out for folder recovery:
- 💾 Disk Drill’s wide file system support makes it effective for recovering folders from virtually any storage device, including flash drives and memory cards (which typically use FAT32 or exFAT file systems), internal hard drives (usually formatted with NTFS), and even advanced storage configurations like RAID arrays and NAS devices (which often use ReFS, EXT4, or BTRFS).
- 📂 When recovering folders from a formatted or corrupted drive, it can be impossible for any data recovery software to retrieve files based on file system information and reconstruct the original folder structure. In such cases, Disk Drill still recovers the individual files that were inside those folders, even if they end up in a flat list rather than their original hierarchy.
- 🎁 Disk Drill isn’t free, but its trial version is genuinely useful. You can run full scans, preview every recoverable file, and even recover up to 100 MB for free. For many users who only need a few important documents or small files from a deleted folder, this limit is more than enough.
- 🖥️ You can run Disk Drill on Windows 11 (x64 & ARM) and Windows 10 (x64 only). Legacy versions are also available for recovering data on older Windows systems.
How to Get Back Deleted Folder in Windows Without 3rd Party Software
Windows includes several built-in recovery tools that can help you retrieve deleted folders without installing third-party software. In fact, some can save the day even in situations when data recovery software isn’t able to.
The main reason why we haven’t told you about them sooner is that most of these methods are essentially backups, and they need to have been set up before you lost your folder to be effective, which, according to our internal data, is more the exception than the rule.
Method 1: Use the File History Feature
If you’ve enabled Windows’ built-in backup tool, called File History, you may be able to retrieve a deleted folder without using third-party software.
When enabled, File History automatically backs up all your libraries (folders like Documents, Music, Pictures, Videos, and Desktop), so any sub-folder deleted from these locations should be backed up. As a result, you can recover deleted folders from desktop in Windows or any other library location using File History backups.
I personally like to access my File History backups through the classic Control Panel:
- Click on the Windows Start menu and type “Control Panel” in the search box.
- Open the Control Panel from the search results.
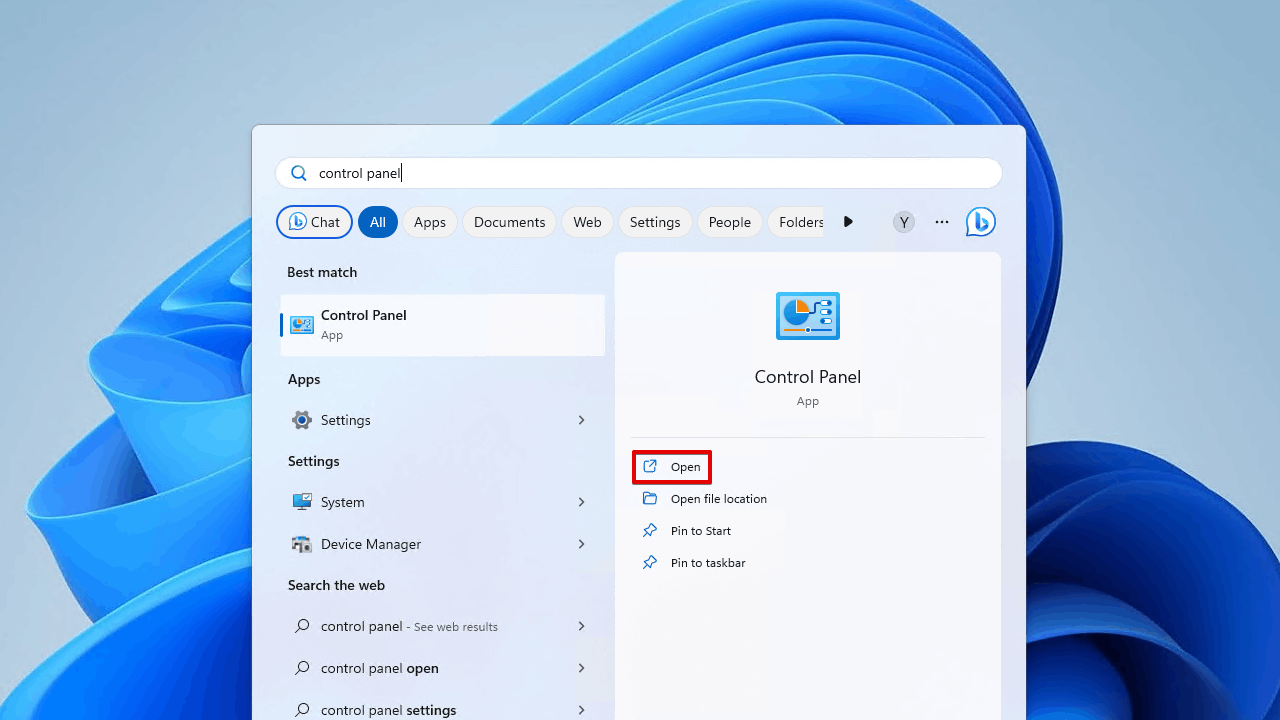
- Type “File History” in the Control Panel search box (top-right corner) and select Restore your files with File History from the results.
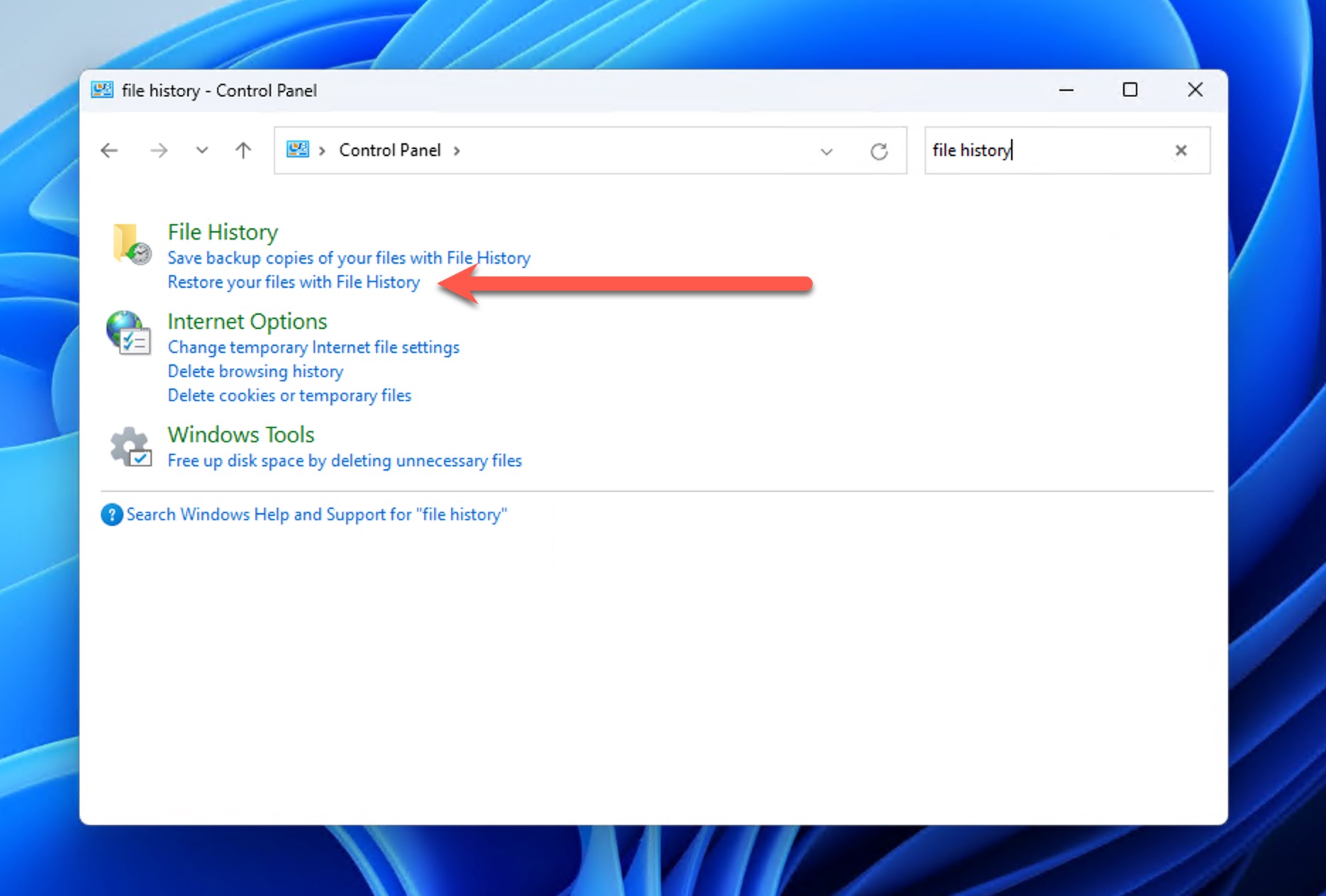
- Navigate to the location where your deleted folder was stored and use the navigation arrows at the bottom to browse through different backup dates.
- Select the folder you want to restore, and click the green restore button at the bottom of the window to recover your deleted folder on Windows.
Method 2: Recover Using the Backup and Restore Feature
Windows 10 and 11 still include the classic Backup and Restore feature that was first introduced with Windows 7, and you can use it to retrieve a deleted folder from both local and network backups.
To recover deleted folders using Backup and Restore:
- Click the Windows Start button and type “Control Panel” in the search box. Select Control Panel from the search results.
- Navigate to System and Maintenance (or System and Security on Windows 11) > Backup and Restore.
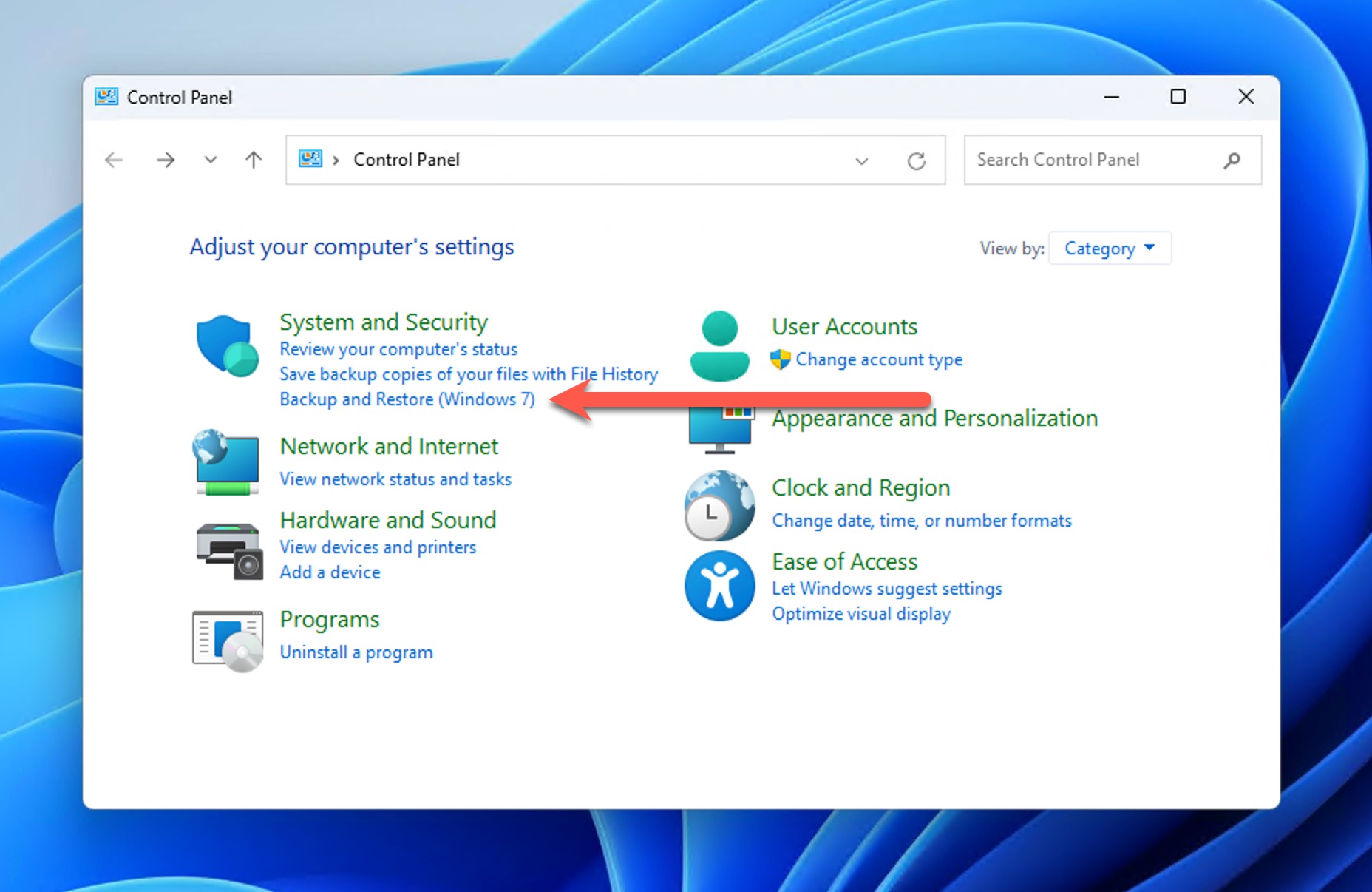
- In the Backup and Restore window, click Restore my files if your backup is detected. If your backup isn’t automatically detected, click Select another backup to restore files from and browse to the location of your backup.
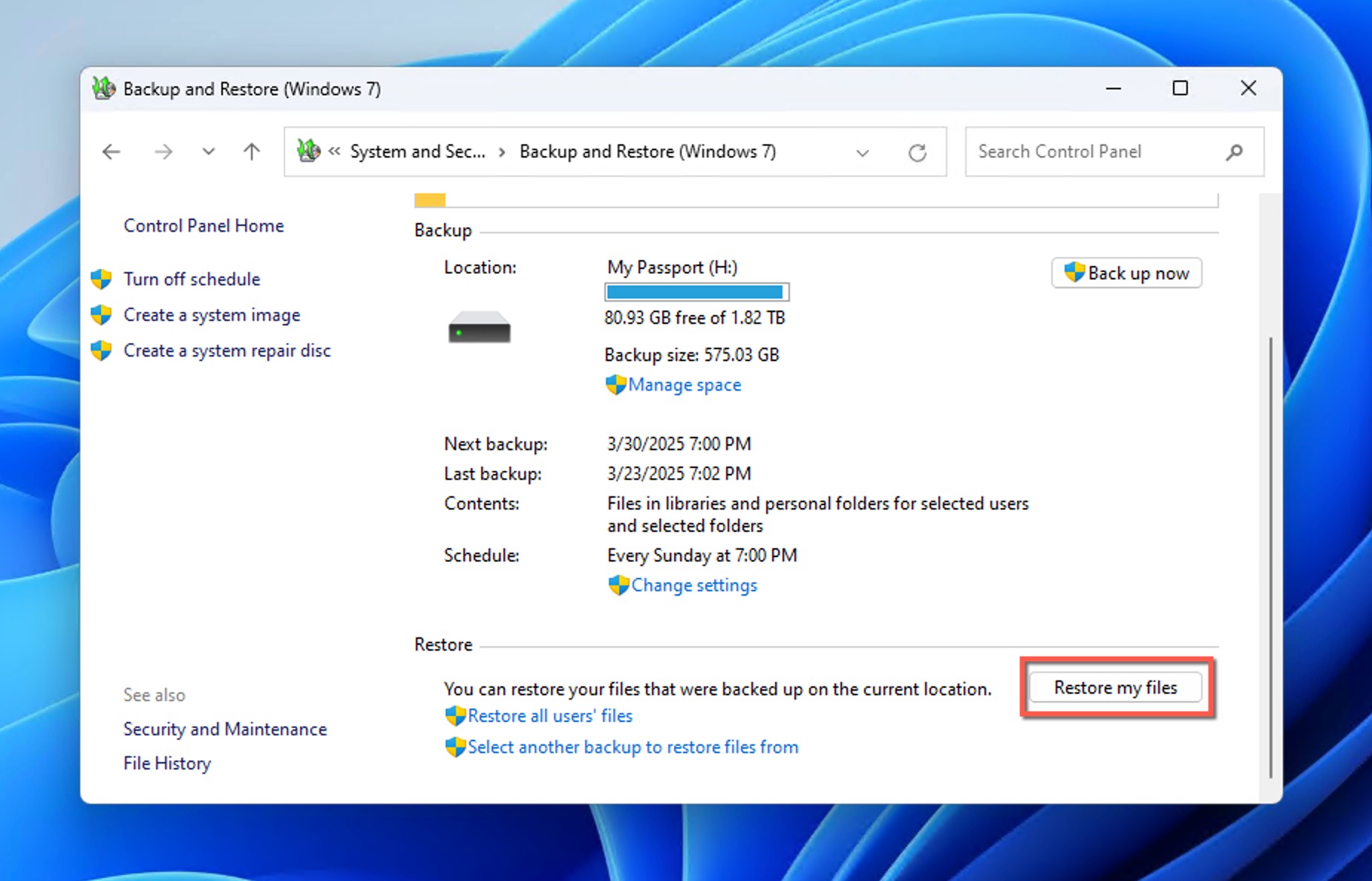
- The recovery wizard will open, allowing you to browse for specific files or folders. Select your deleted folder and choose whether to restore to the original location or a new location.
Method 3: Try the Windows File Recovery Tool
Microsoft provides its own data recovery tool for Windows, called Windows File Recovery, and you can use it to recover the content of any permanently deleted folder.
Additionally, our testing showed that the tool is mainly effective for recovering deleted data from NTFS (system) drives. If your folder was lost during formatting or deleted from another file system like FAT32 or exFAT, the software’s effectiveness drops significantly.
Still, Windows File Recovery is completely free, so there’s no reason not to try it. For a detailed breakdown of its capabilities and limitations, check out our Windows File Recovery review.
To install Windows File Recovery, you need Windows 10 2004 and above. If you meet this requirement, then you can follow these steps:
- Launch Microsoft Store and look for “Windows File Recovery” using the search bar.
- Install the Windows File Recovery tool.
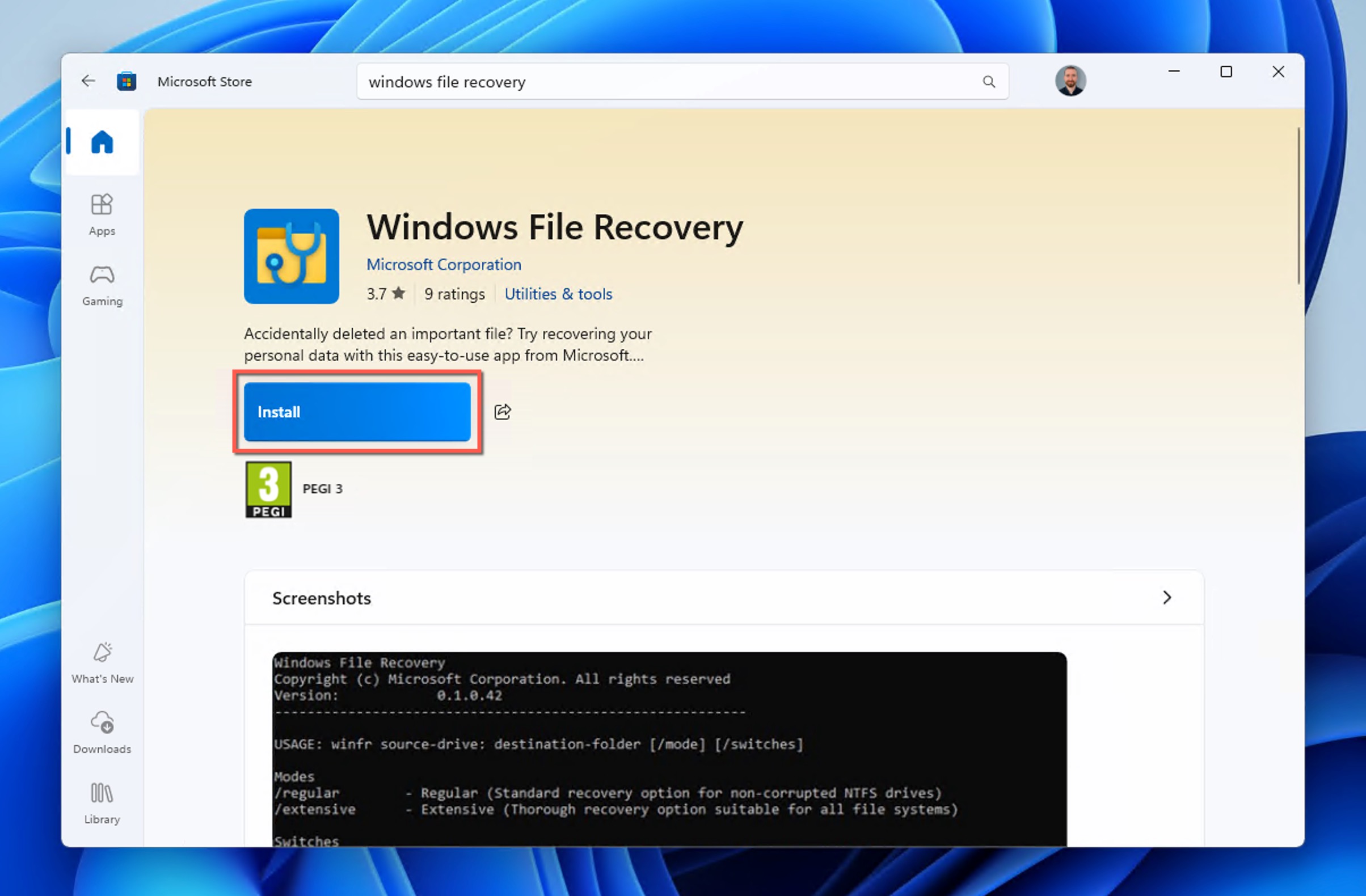
- Press the Windows key, type “Windows File Recovery” and select it from the results.
- Use the following command syntax to recover your deleted folder: winfr source-drive: destination-drive: /mode /switches
For example, here’s how you can recover a deleted Documents folder using Regular mode:
winfr C: E: /regular /n \Users\YourUsername\Documents\
This command would attempt to recover all deleted files and folders that were located in the Documents folder (under your user profile) from the C: drive, and restore them onto the D: drive. You can also recover only specific file types from a deleted folder:
winfr C: E: /regular /n \Path\To\Folder\*.docx /n \Path\To\Folder\*.pdf
The command above recovers Word documents and PDFs from a specific folder location.
Method 4: Download the Folder from OneDrive
Microsoft OneDrive is a cloud storage service built directly into Windows 10 and 11. When enabled, it automatically syncs files from designated folders on your computer to the cloud. If your deleted folder was stored in your OneDrive directory, a backup copy might still exist online even after local deletion.
We’ve seen OneDrive save the day in the following situations:
- The storage device has some underlying issues that cause it to freeze/crash the operating system or recovery tools.
- You want to recover a deleted folder from a OneDrive-synchronized location on an encrypted storage device but either don’t know how to do it or don’t remember the correct decryption password.
- Your recovered folder contains damaged files that won’t open, but there are clean copies in your OneDrive cloud storage.
To download the folder from OneDrive, check if the folder still exists in the cloud storage:
- Open your web browser and go to https://onedrive.live.com/
- Sign in with your Microsoft account credentials (the same account you use on your Windows computer).
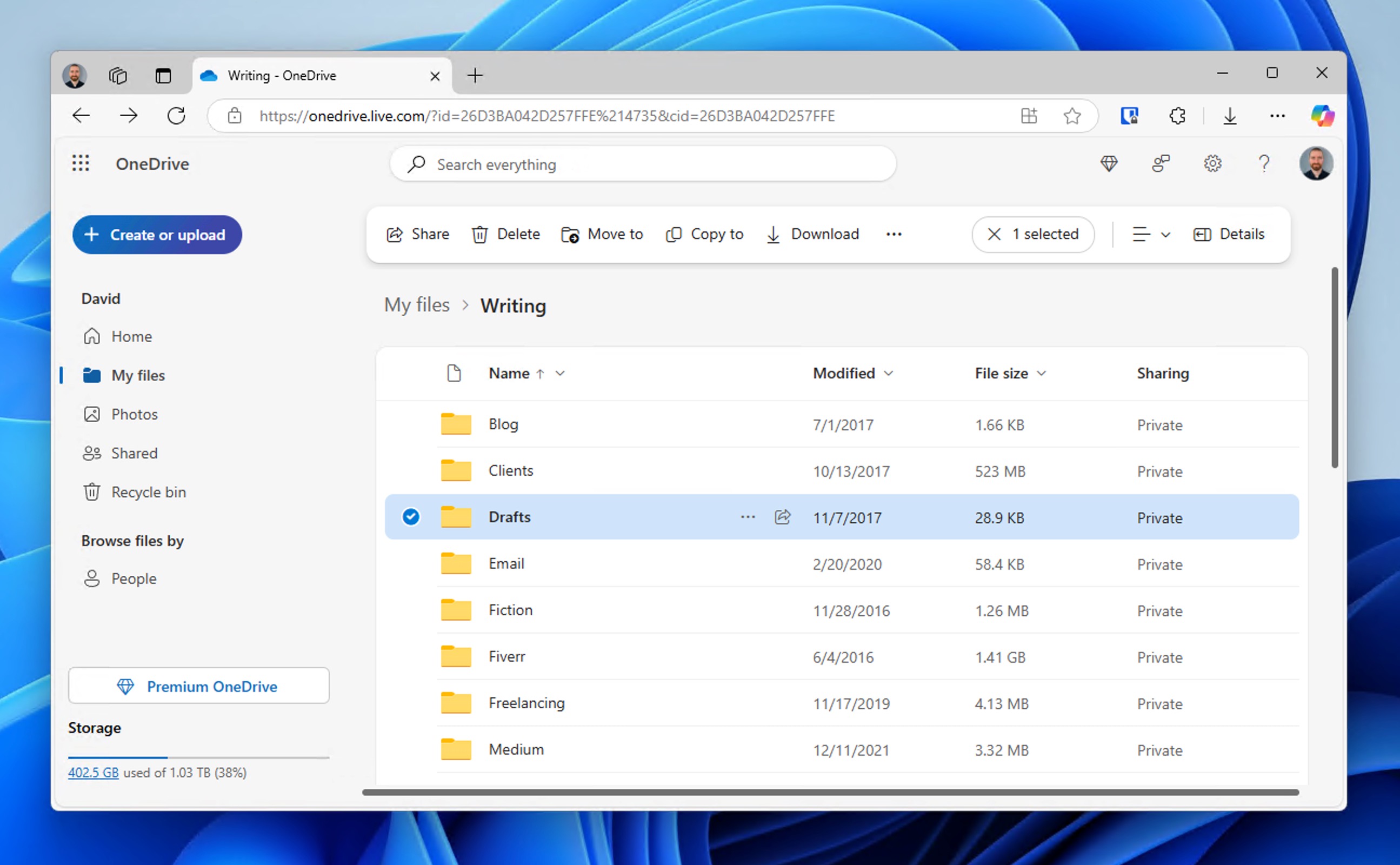
- Browse through your OneDrive files to locate the deleted folder. If it’s still visible in the cloud but not on your computer, it’s possible the deletion hasn’t synced yet.
If you find it still present in OneDrive, then you should download it to your device. If not, then also check the OneDrive cloud Recycle Bin:
- While still on the OneDrive website, look for Recycle bin in the left navigation pane.
- Locate your deleted folder. You can use the search function at the top if you have many deleted items.
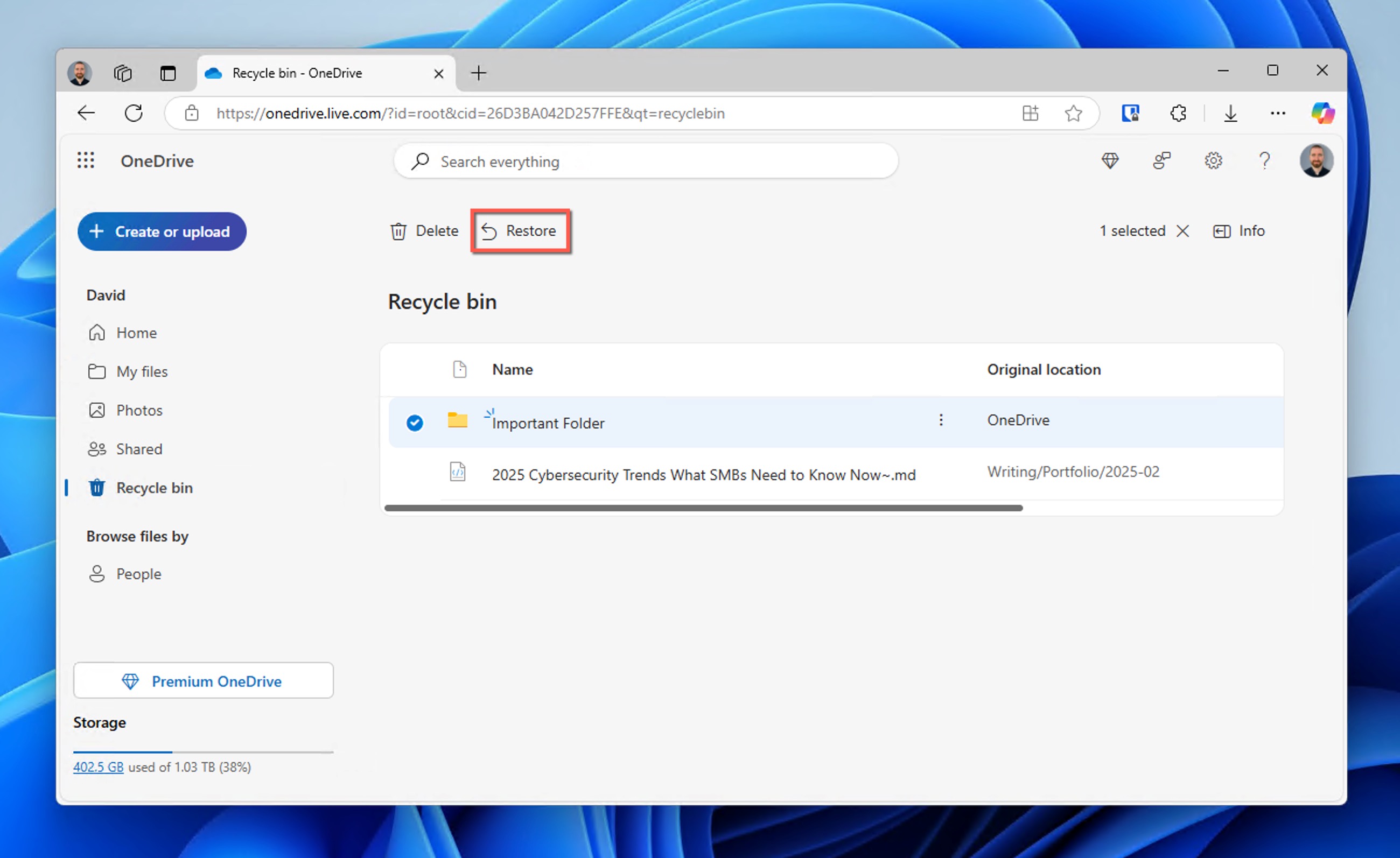
- Select the folder by clicking on it, then click the Restore button.
Once restored, the folder will automatically sync back to your computer’s OneDrive folder.
Method 5: Consider Contacting Data Recovery Professionals to Recover Your Folder

While the DIY recovery techniques described in this article are all fairly straightforward and capable of delivering great results, they aren’t your only option. You can also pay data recovery professionals to get the folder back for you.
Professional data recovery is a great choice (and often the only one) to recover the permanently deleted folder when dealing with:
- Failed recovery attempts: If you’ve tried using data recovery software but it either doesn’t find your folder or recovers corrupted versions of your files.
- Lack of technical confidence: If you’re uncomfortable performing the technical steps required for DIY recovery and don’t want to risk something going wrong.
- Physical damage: If your storage device is making unusual noises, not being recognized by your computer, or showing other signs of physical failure. Professional recovery technicians have specialized equipment to recover data from physically damaged drives in clean-room environments.
Even though professional data recovery is significantly more expensive than the DIY methods described earlier in this article, all reputable services won’t charge if they can’t recover your files, and they will provide you with an accurate price quote beforehand to prevent unpleasant surprises.
FAQ
When you delete a folder, Windows typically moves it to the Recycle Bin. However, a folder gets permanently deleted without going to the Recycle Bin first if you use Shift+Delete, exceed the Recycle Bin’s size limit, delete from SD cards/USB flash drives, or delete using a Terminal command. Even if you’ve accidentally emptied the Recycle Bin with important folders still inside, you may still be able to recover files from the Recycle Bin after emptying it using data recovery software because Windows doesn’t immediately erase the actual data.
No, your folder is not guaranteed to be lost forever. Despite the fact that using Shift+Delete bypasses the Recycle Bin and performs an immediate deletion, the actual data remains physically on your storage device until the physical storage blocks are overwritten with new data, which gives you a chance to recover your folder using specialized data recovery software. For more information, check out our article on how to recover Shift+deleted files in Windows.
Your folder may not be in the Recycle Bin if you deleted it using Shift+Delete, if it exceeded the Recycle Bin size limit, if it was deleted from a removable drive, or if it was deleted via Command Prompt. In such situations, you can use data recovery software to directly scan the storage device from which the folder was deleted. If it still hasn’t been overwritten, then you’ll be able to recover it.
No, files deleted from USB drives and SD cards typically bypass the Recycle Bin and are deleted immediately. However, recovery is still possible using data recovery software since the data isn’t immediately erased from the drive.
System Restore only affects system files, registry settings, and installed programs. It doesn’t restore personal files or folders that have been deleted. You’ll need to a different recovery methods, such as the File History feature or data recovery software like Disk Drill.
Yes, SSDs make file recovery more challenging due to TRIM functionality, which efficiently wipes deleted data blocks to improve performance. On SSDs with TRIM enabled (most modern SSDs), permanently deleted files may be wiped within minutes or hours of deletion, which is why it’s essential to begin the recovery process as soon as possible.